The Diamond Industry At A Crossroads
The global diamond industry is going through a seismic shift. With synthetic or lab-grown diamonds becoming more and more affordable and indistinguishable from mined ones, the traditional diamond trade is confronted by challenges unlike any in its history. What was once a luxury built on rarity is now an industry looking at the chance of reinvention.

The Rise Of Lab-Grown Diamonds
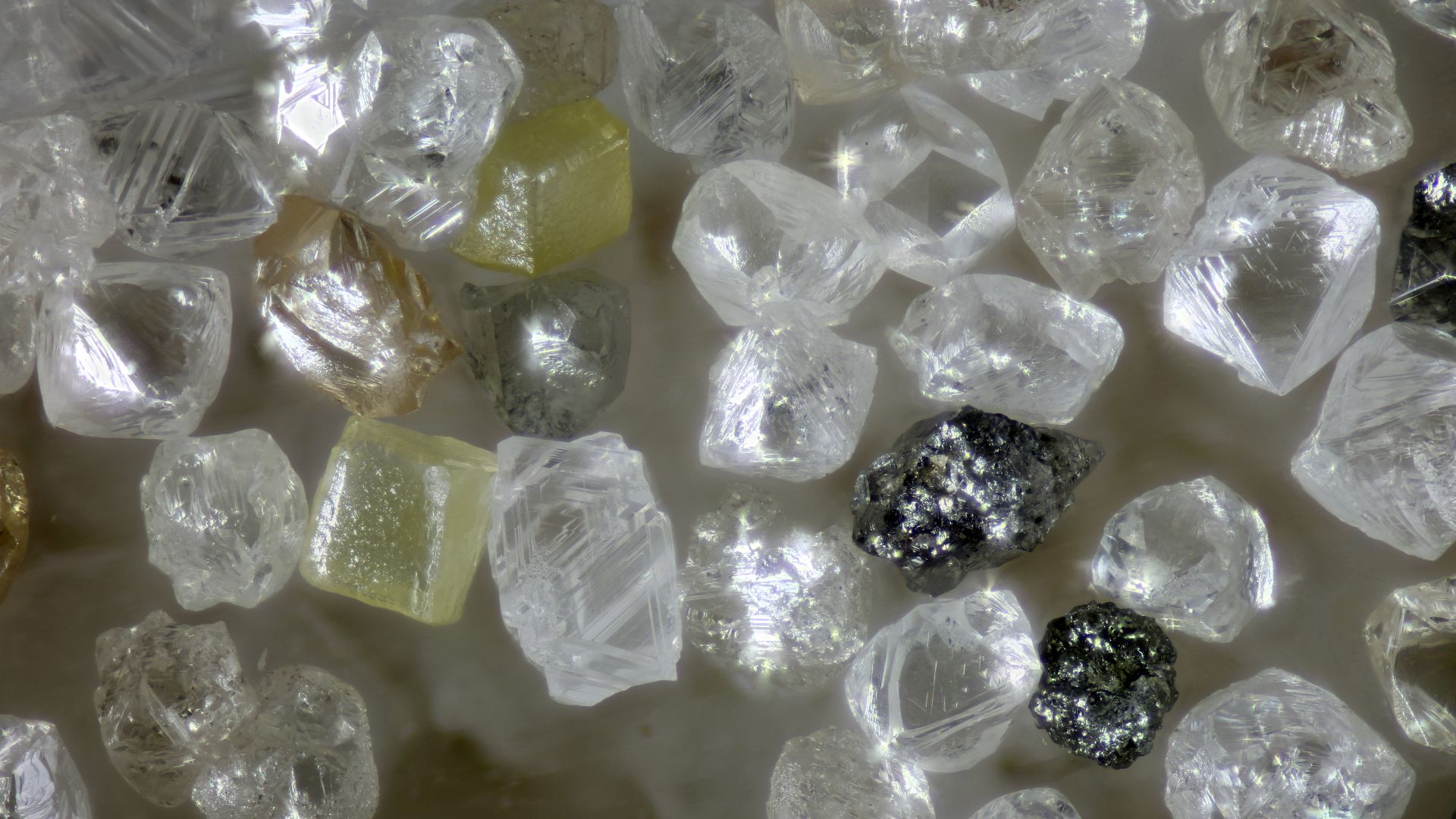
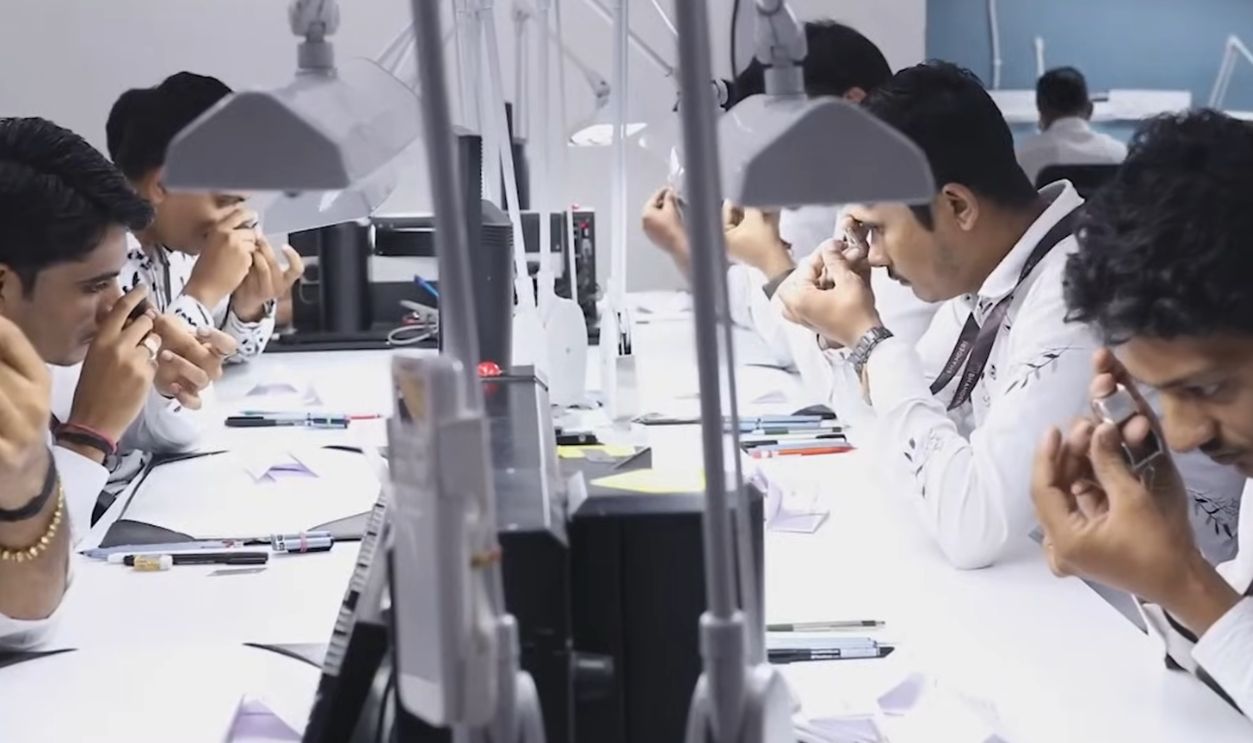
Technological breakthroughs have allowed synthetic diamonds to match mined ones in brilliance, durability, and chemical structure. Created in controlled environments using high-pressure, high-temperature or chemical vapor deposition methods, these gemstones can now be mass-produced at only a fraction of the cost.
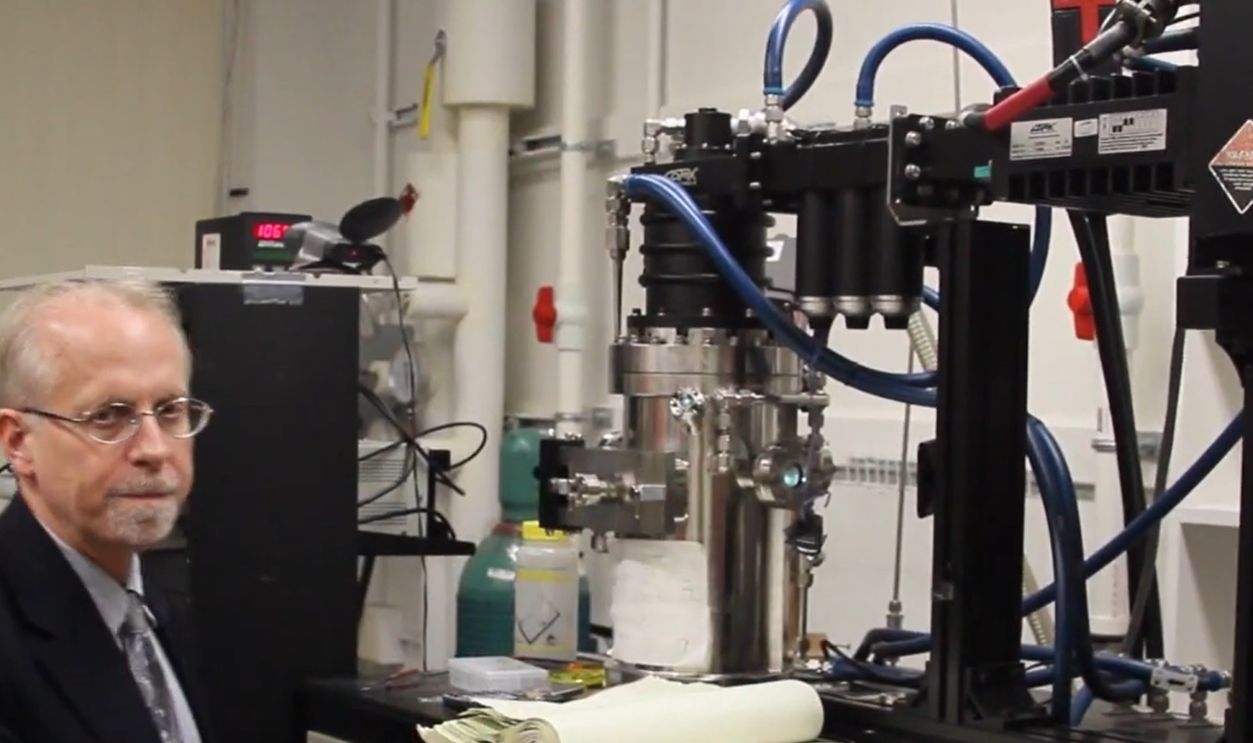 Growing Synthetic Diamonds, Chemical & Engineering News
Growing Synthetic Diamonds, Chemical & Engineering News
Changing Consumer Preferences
More consumers, especially of the younger generation, are opting to buy lab-grown diamonds for ethical and financial reasons. With identical physical properties, fewer impurities, and lower prices, synthetic diamonds aren’t seen as inferior substitutes but as the superior choice by many modern shoppers.
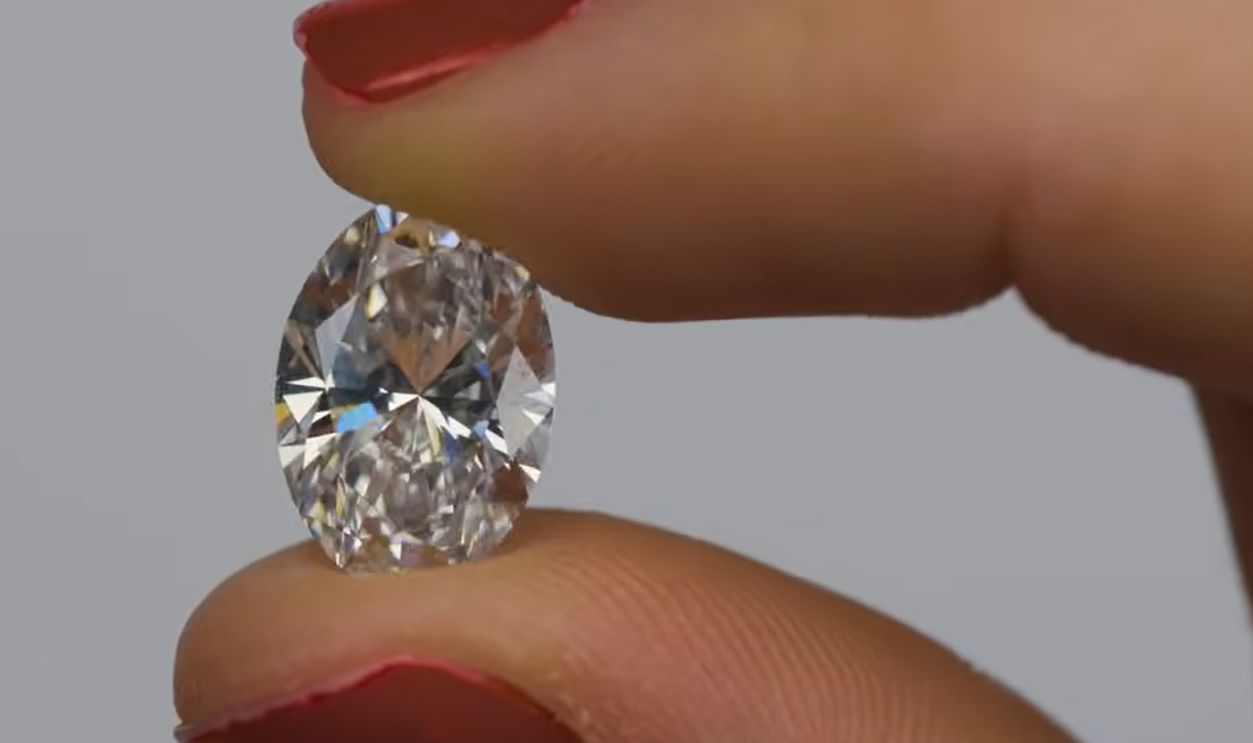 HOW DIAMONDS GROW | UNBOXING LAB GROWN DIAMONDS, Gemstones
HOW DIAMONDS GROW | UNBOXING LAB GROWN DIAMONDS, Gemstones
Synthetic Diamonds: Environmental Advantages
Unlike mined diamonds, lab-grown gems don’t need any large-scale land disturbance or energy–intensive excavation. The environmental footprint is much smaller, offering consumers an appealing alternative at a time when sustainability is a driver of consumer behavior.
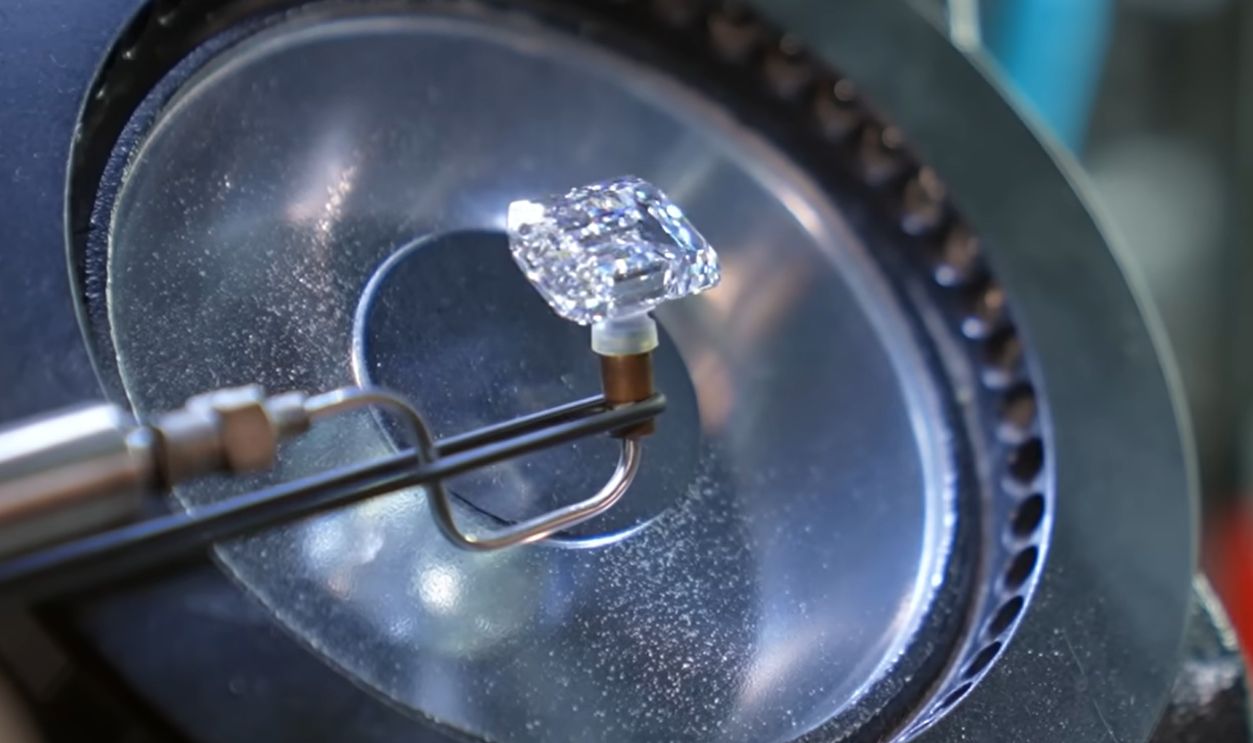 Inside India’s lab-grown diamond industry - BBC News, BBC News
Inside India’s lab-grown diamond industry - BBC News, BBC News
Ethical Concerns And Human Rights
One of the biggest appeals of lab-grown diamonds is their dissociation from the so-called ‘blood diamond’ trade. Synthetic gems do away entirely with the human exploitation often associated with diamond mining in war-torn regions. For many consumers, that ethical clarity is worth a lot more than a stone’s carat rating.
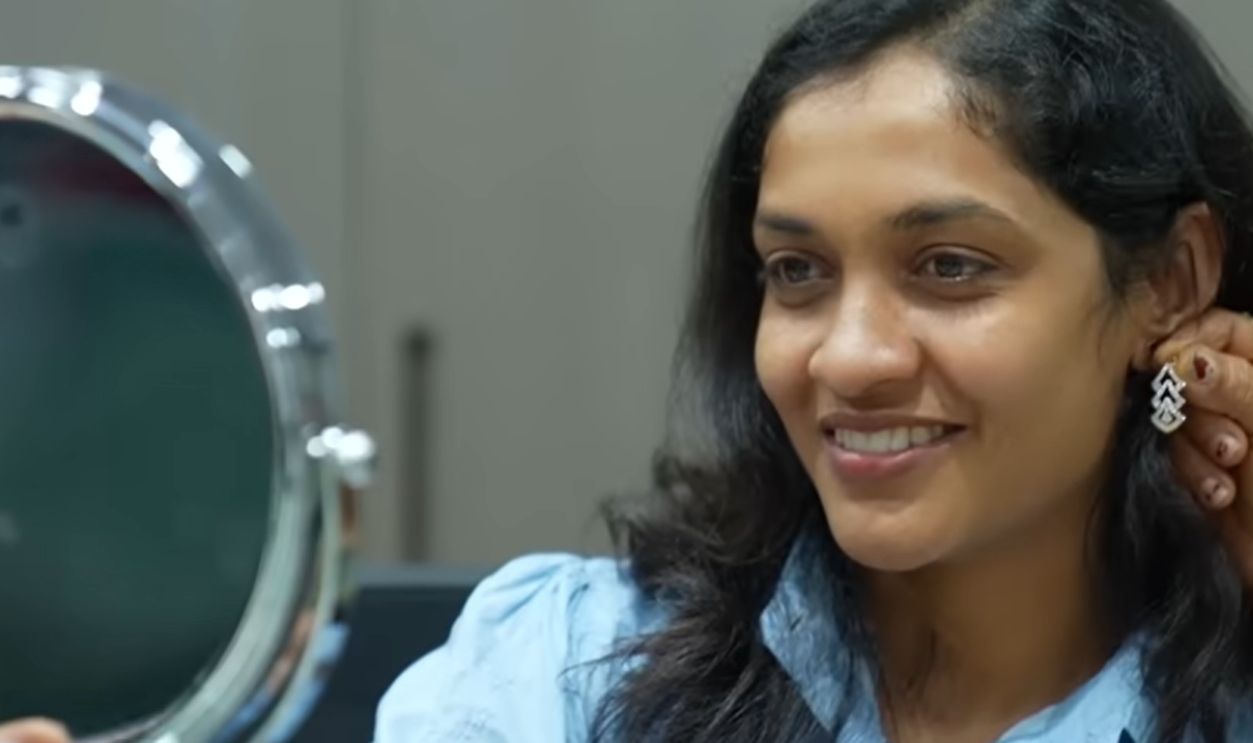 Inside India’s lab-grown diamond industry - BBC News, BBC News
Inside India’s lab-grown diamond industry - BBC News, BBC News
Cost Efficiency And Market Disruption
Lab-grown diamonds can cost up to 80% less than their mined counterparts. This price gap has forced traditional retailers to adapt, which is reshaping the luxury market. Companies like Pandora and Brilliant Earth have already transitioned to fully synthetic diamond lines.
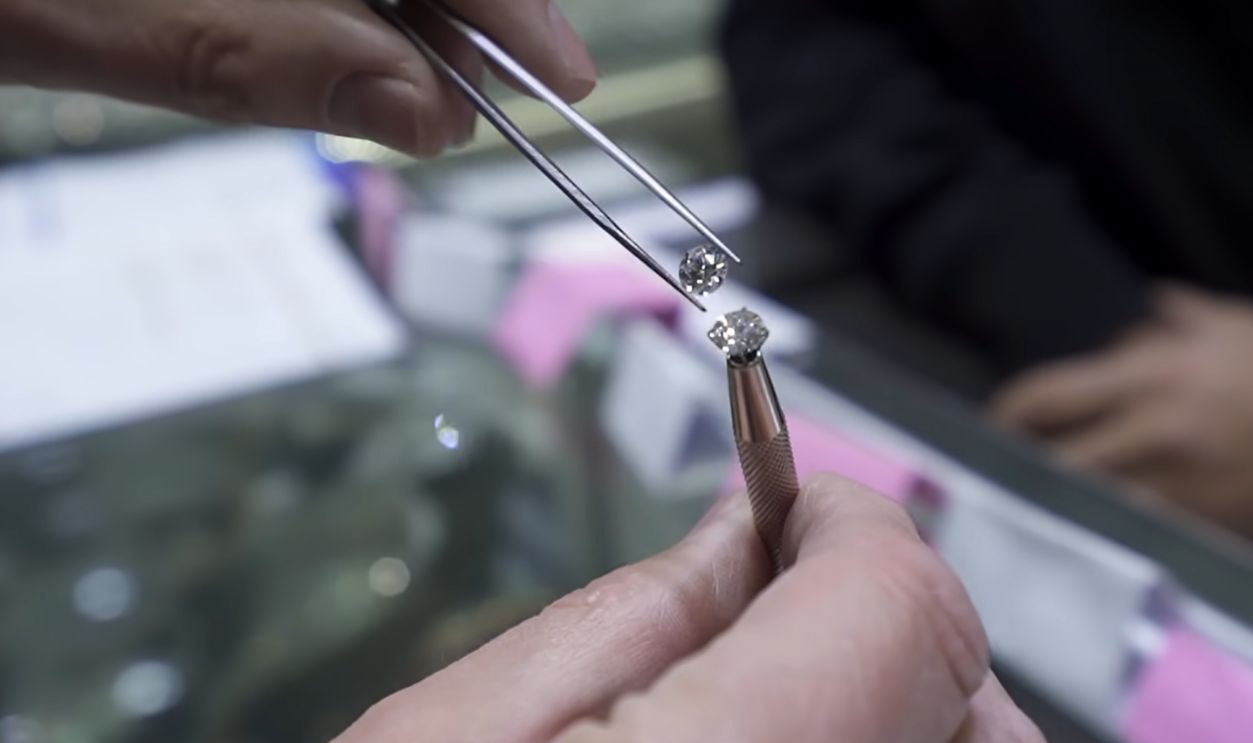 Natural Diamonds vs Lab Grown: Which Should You Buy?, ProducerMichael
Natural Diamonds vs Lab Grown: Which Should You Buy?, ProducerMichael
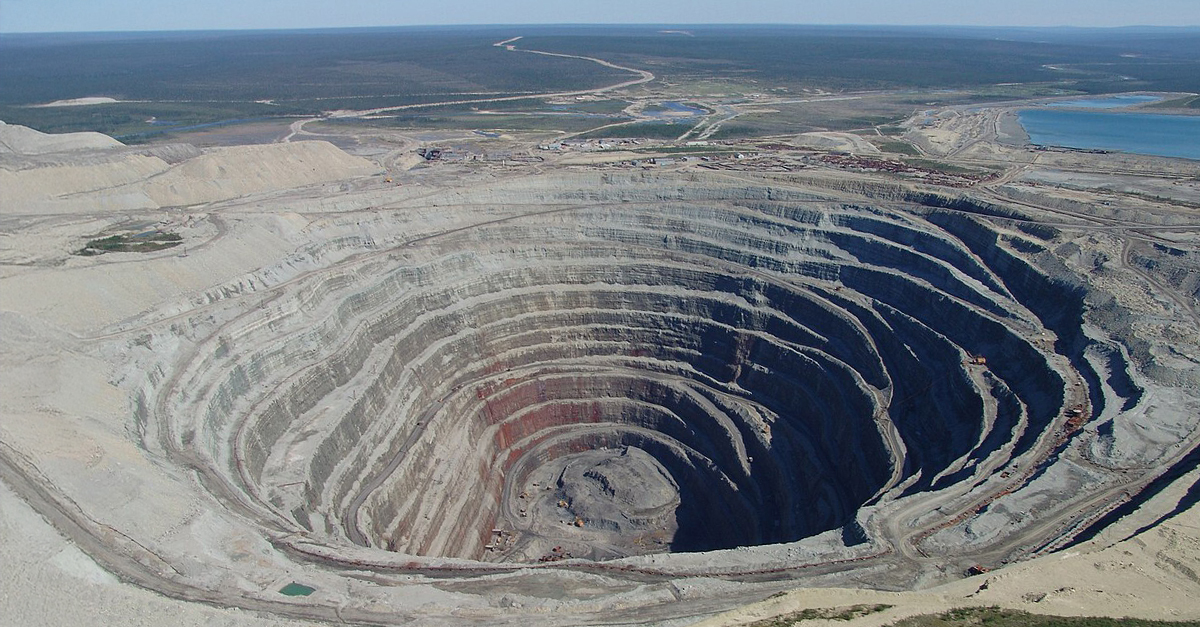
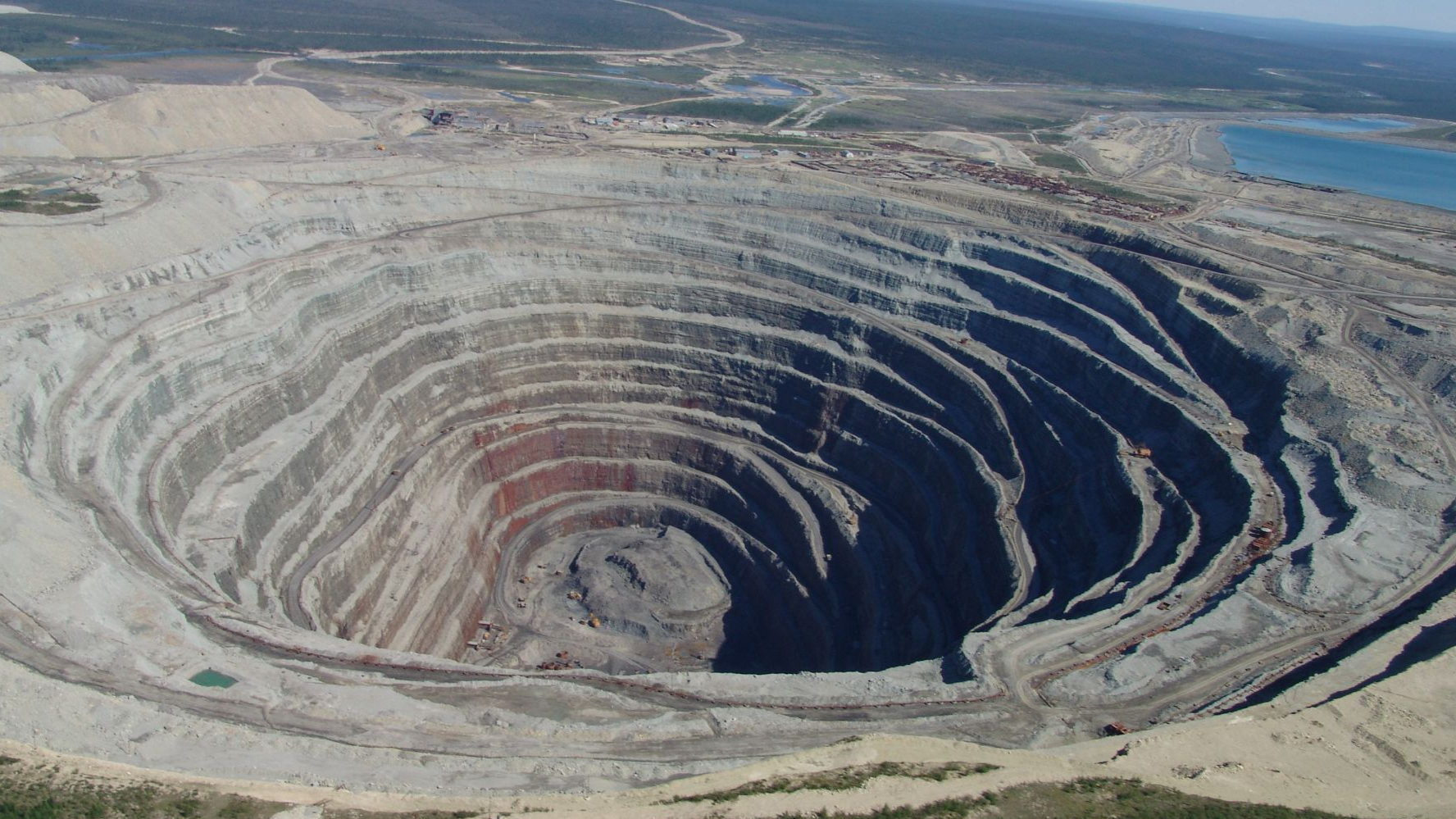
Mined Diamonds On The Decline
Big mining companies like De Beers and Alrosa have already reported declining revenues and reduced operations. As production slows and synthetic alternatives gain popularity, traditional diamond mining faces an existential crisis somewhat like the coal industry’s decline.
Why Mined Diamonds Still Matter
Despite the attention on synthetic gems, natural diamonds still hold a lot of symbolic and financial value. Collectors and investors view mined stones as rare natural assets, similar to the way gold is regarded. That rarity ensures that mined diamonds won’t completely vanish anytime soon.
Culture, Legacy, And Tradition
For centuries natural diamonds have retained their symbolic status of love, and commitment. That cultural weight still has an influence on purchasing decisions. A lot of engagement ring buyers still insist on a ‘real’ diamond, believing that authenticity carries greater emotional weight.
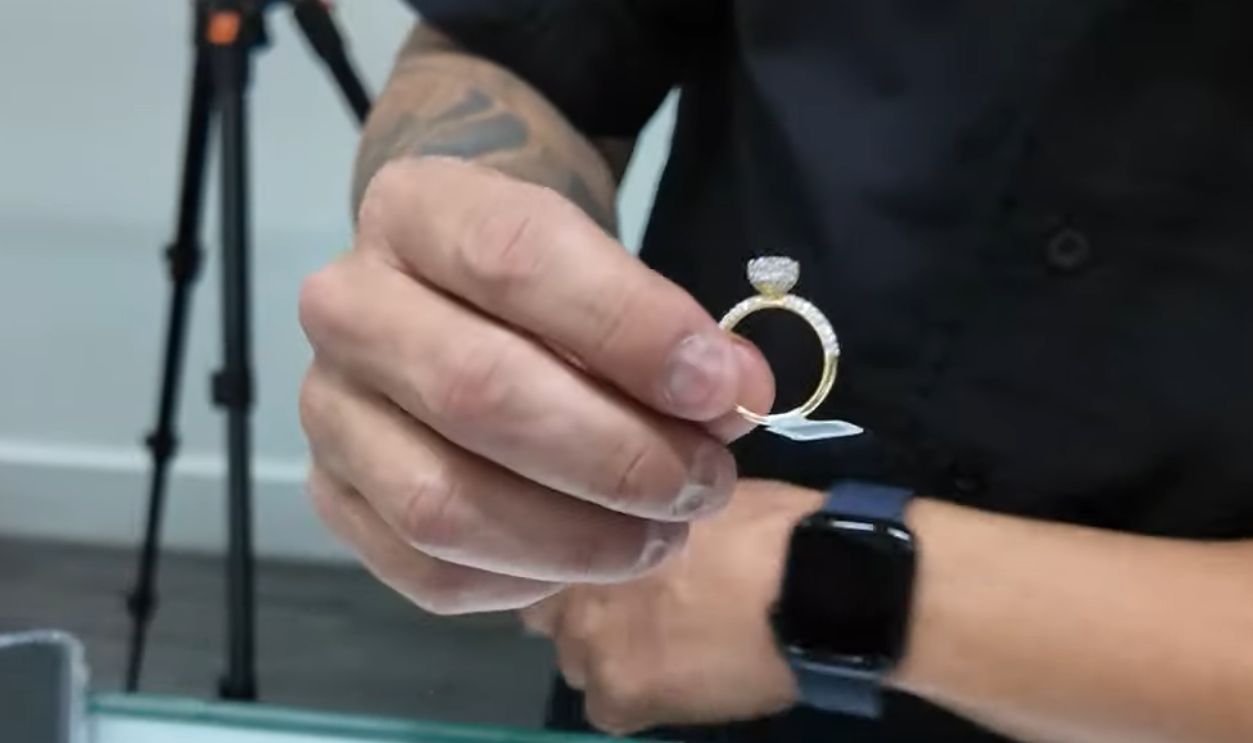 Making The PERFECT Diamond Engagement RING!, Gustavo Villa Jewelry
Making The PERFECT Diamond Engagement RING!, Gustavo Villa Jewelry
Investor Uncertainty In The Diamond Sector
With all these factors in play, the diamond market is clearly in flux. Some investors are divesting from mining stocks, while others see an opportunity for diversification toward lab-grown production facilities. The uncertainty has led to more volatile pricing and new investment strategies around the world.
Synthetic Diamonds In Industry
Beyond jewelry, synthetic diamonds have a wide range of industrial uses that extend into semiconductors, optics, and thermal conductivity solutions. Their hardness and precision make them essential in manufacturing, which could drive even greater production in the coming decade.
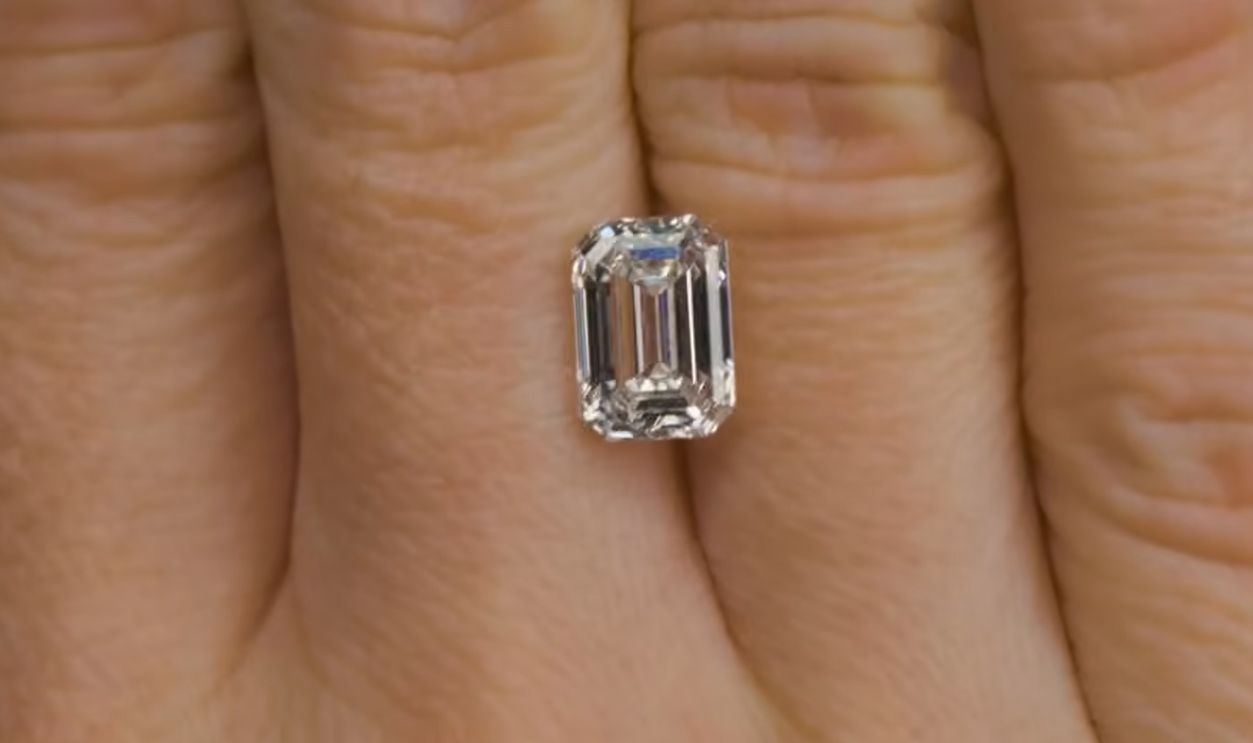 HOW DIAMONDS GROW | UNBOXING LAB GROWN DIAMONDS, Gemstones
HOW DIAMONDS GROW | UNBOXING LAB GROWN DIAMONDS, Gemstones
Synthetic Diamond Boom: The China Factor
China has recently emerged as the global leader in lab-grown diamond production. With its vast manufacturing capacity and government incentives, Chinese companies are flooding the global market for synthetics, undercutting prices and forcing Western producers to innovate or go under.
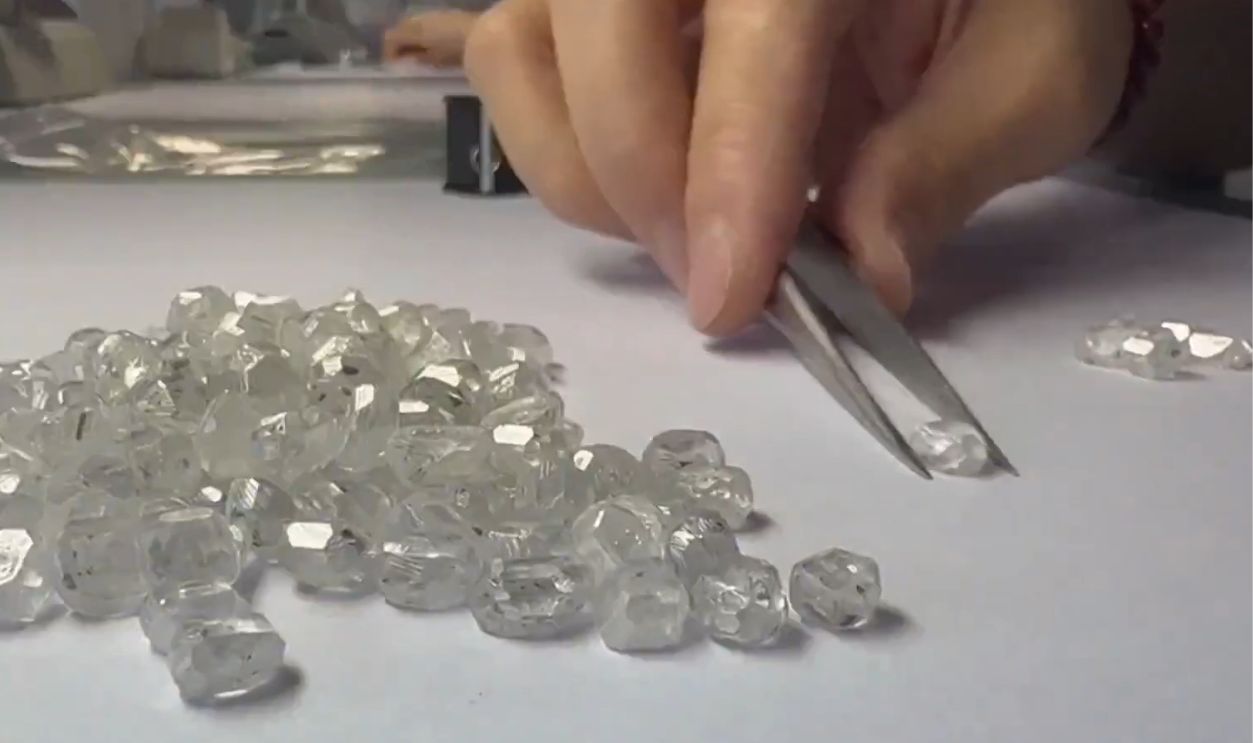 China's Lab-Grown Diamonds Sparkle on Global Stage, Switch TV News
China's Lab-Grown Diamonds Sparkle on Global Stage, Switch TV News
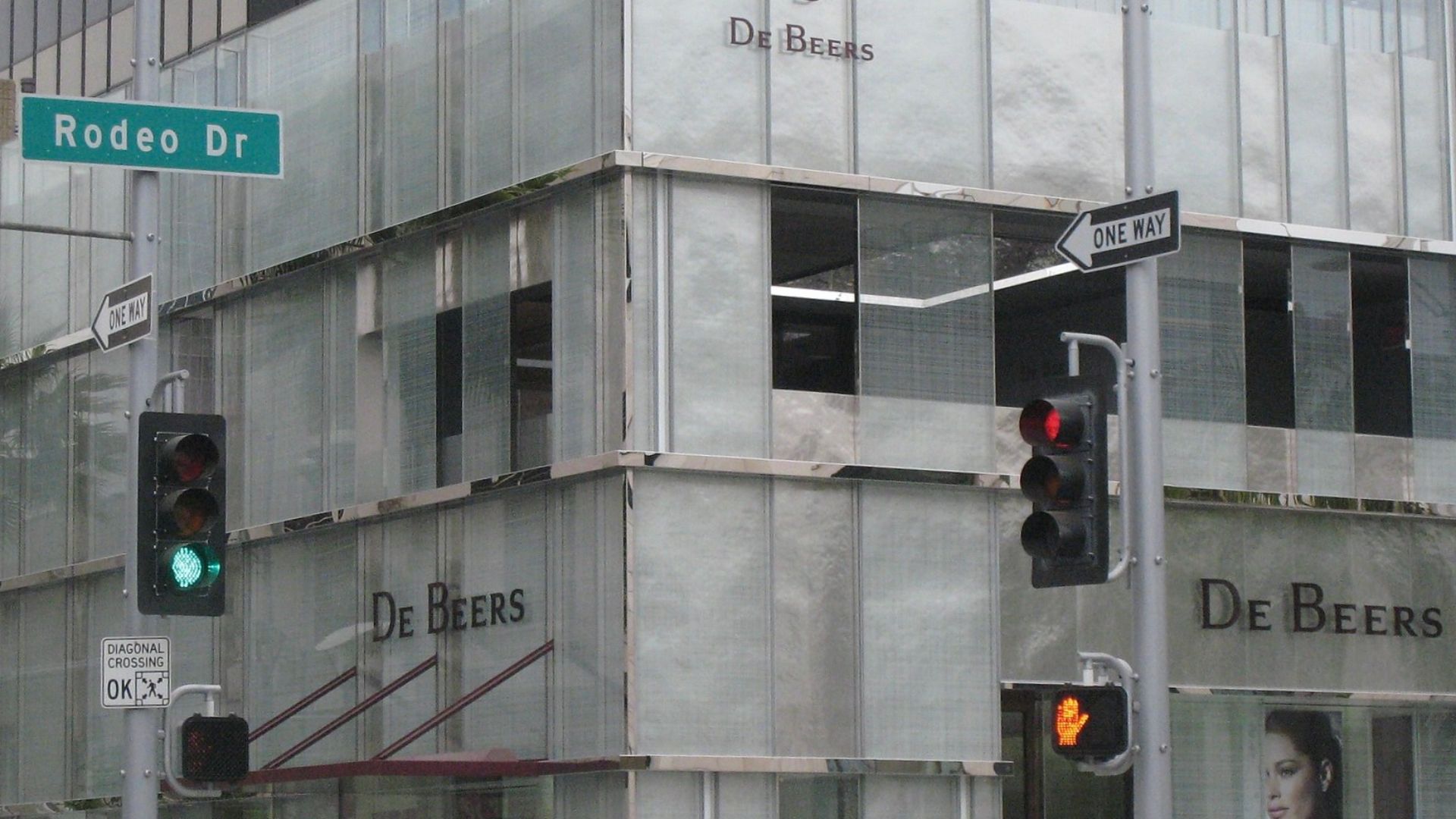
De Beers’ Strategic Pivot
Even De Beers, once the flagship company of mined diamonds, now sells its own line of lab-grown gems under the Lightbox brand. Their canny move signals that the traditional industry’s biggest players have already recognized the inevitability of synthetic competition.
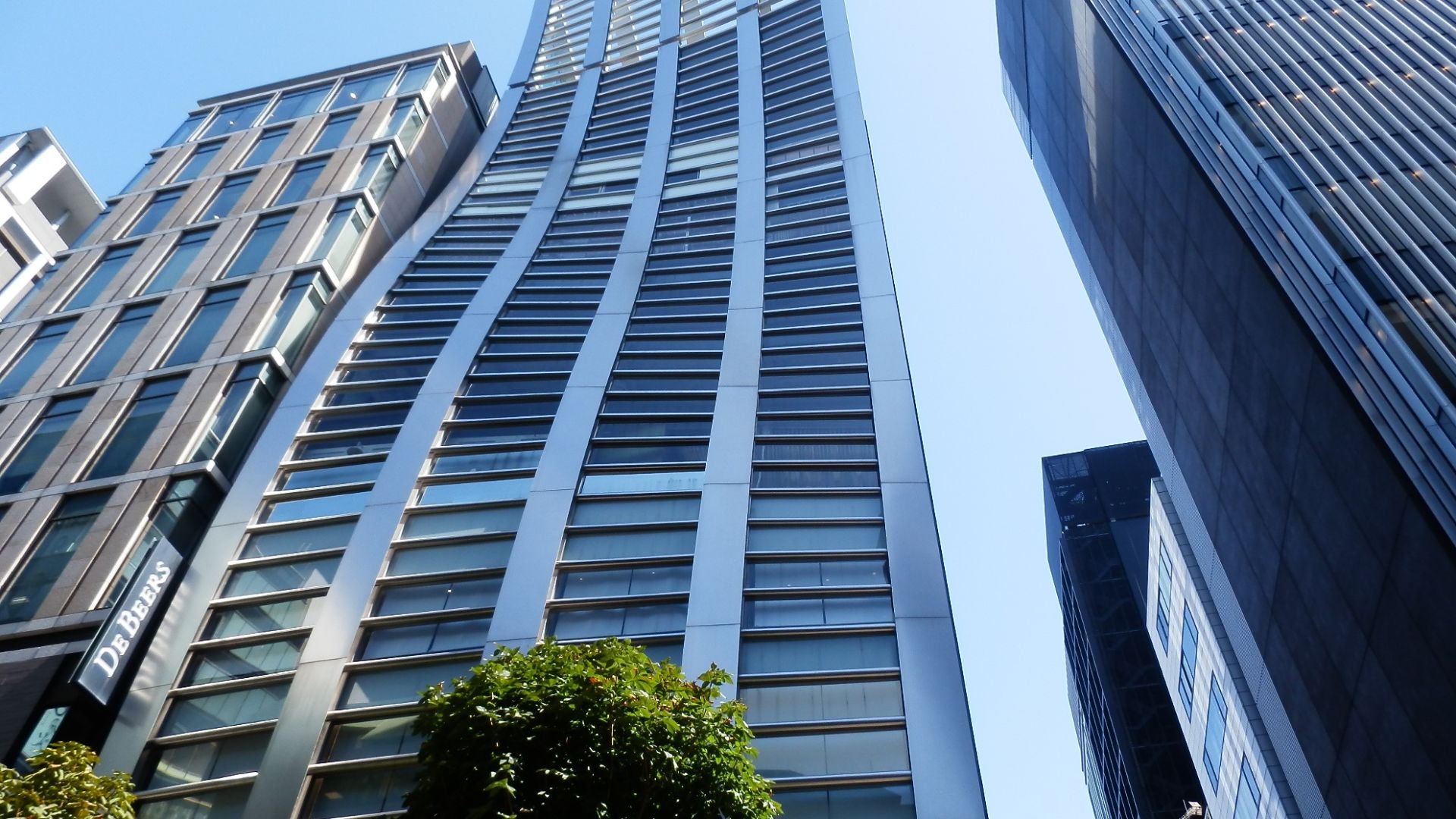 naobim from Japan, Wikimedia Commons
naobim from Japan, Wikimedia Commons
Energy Costs And Sustainability Concerns
While lab-grown diamonds are cleaner than mining, they do still consume a significant amount of energy, especially electricity for high-pressure systems. The sustainability advantage really depends on how that energy is generated; coal-powered factories would represent a clear loss of environmental benefits.
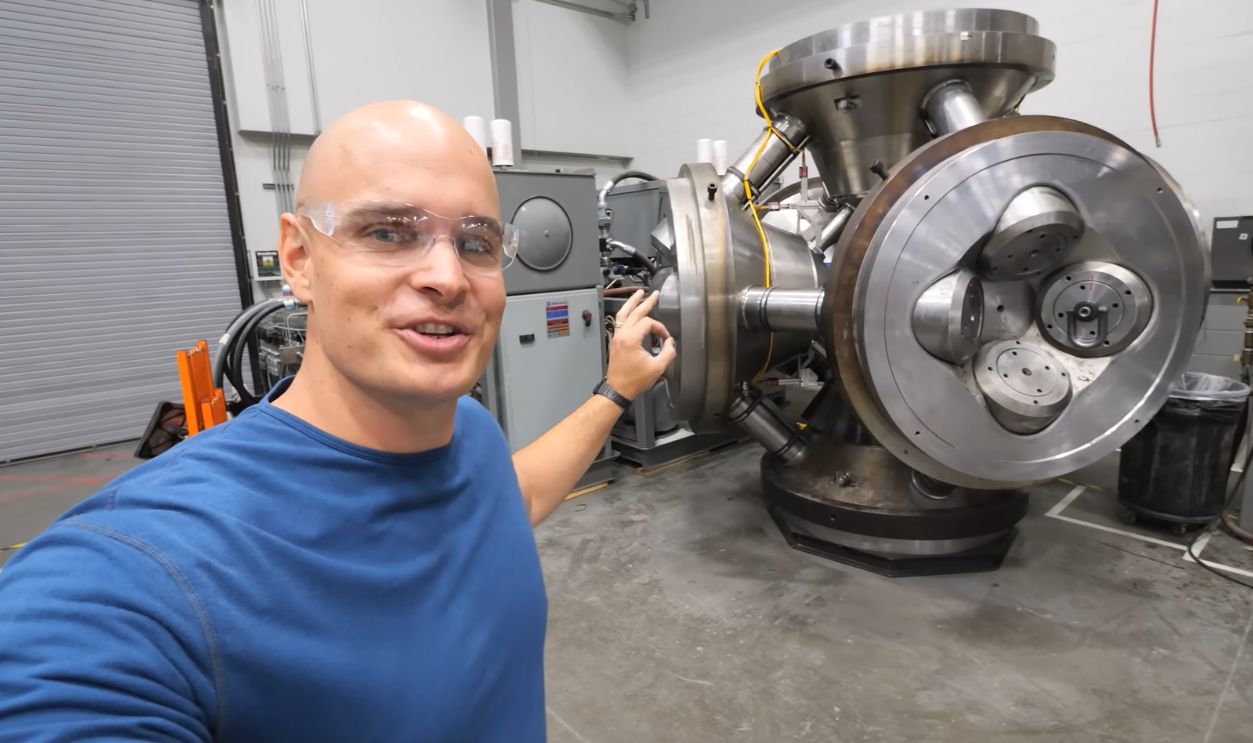 How to Make a Real Diamond - (Not Clickbait), JerryRigEverything
How to Make a Real Diamond - (Not Clickbait), JerryRigEverything
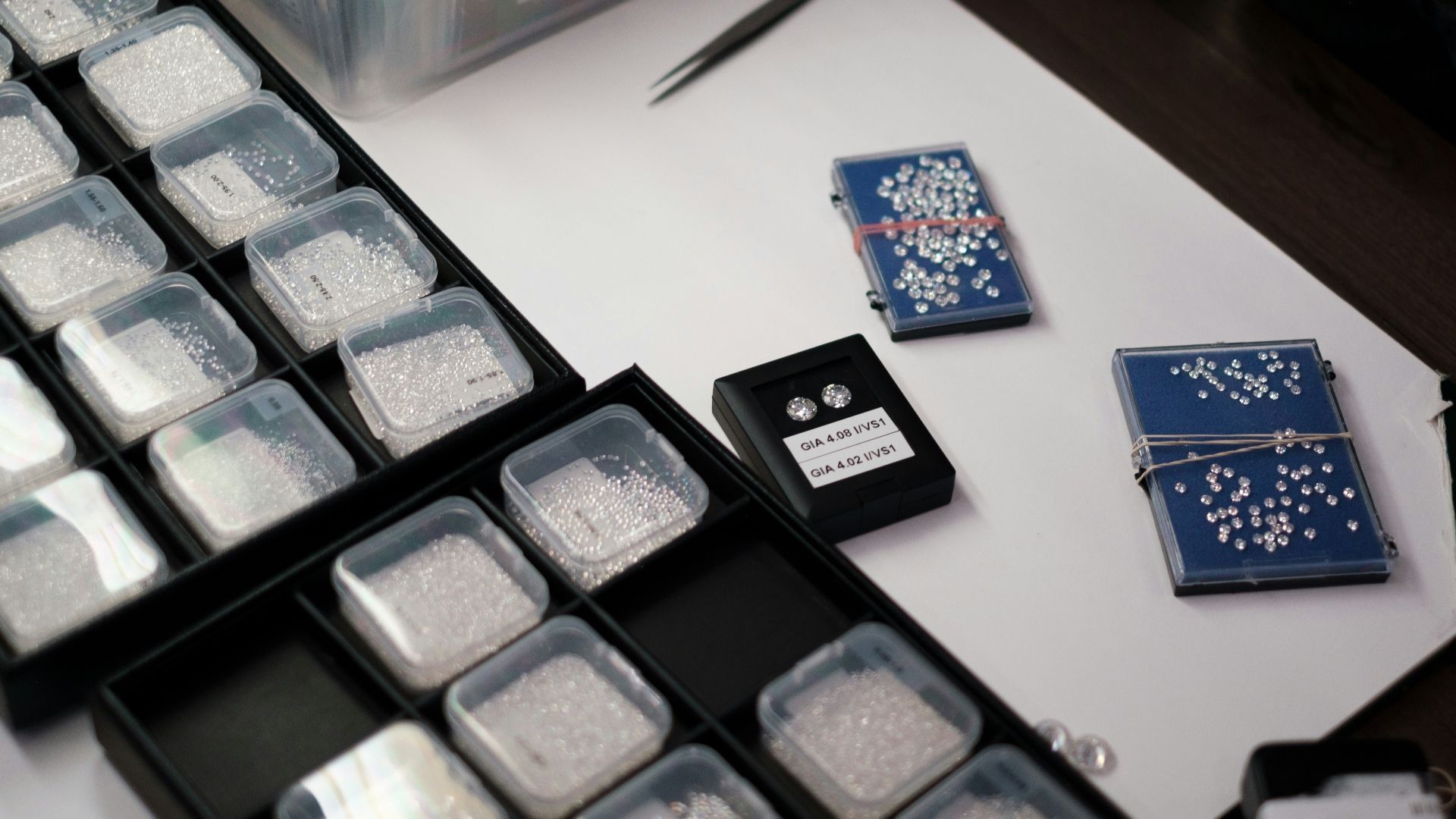
The Shrinking Distinction Between Real And Lab-Grown
The technology of gemstone identification and appraisal has advanced to such a degree that even trained experts now struggle to distinguish lab-grown diamonds without specialized instruments. This blurring of the line has made certification and transparency increasingly critical in the modern diamond trade.
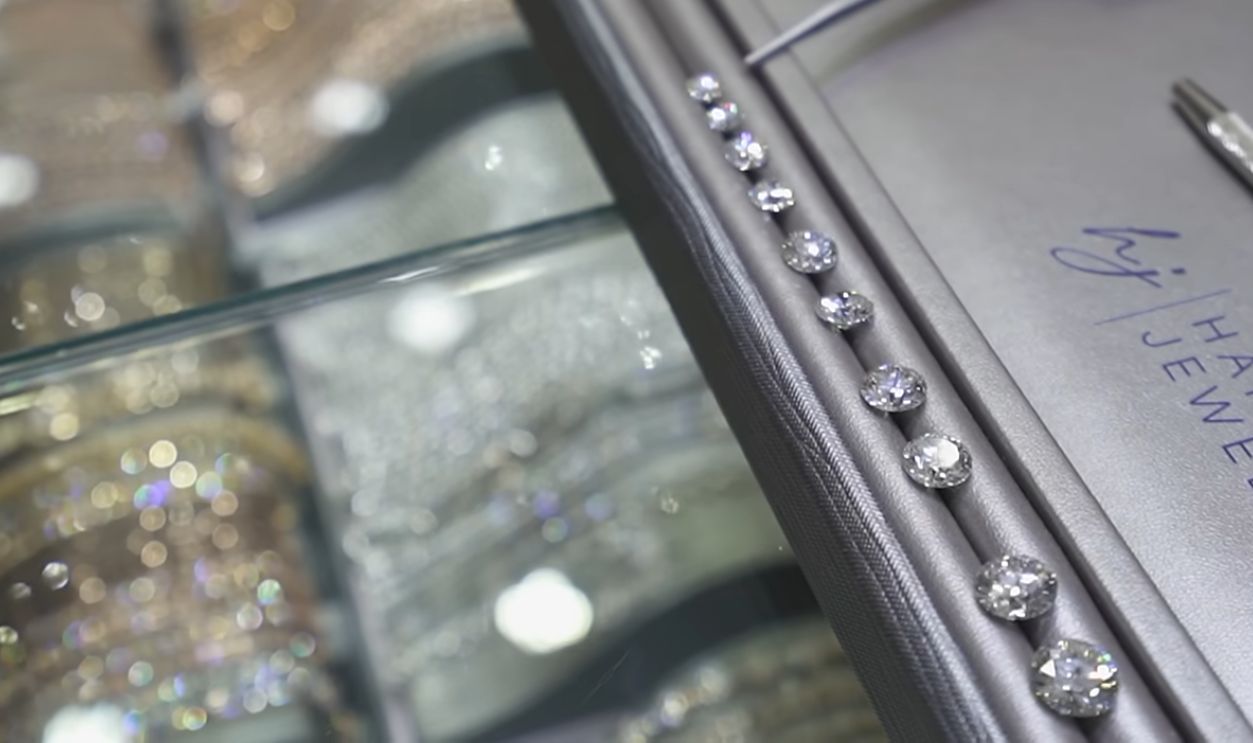 Natural Diamonds vs Lab Grown: Which Should You Buy?, ProducerMichael
Natural Diamonds vs Lab Grown: Which Should You Buy?, ProducerMichael
Regulatory And Disclosure Challenges
Governments and industry watchdogs are still catching up to the rapid growth of the lab-grown diamond market. Mislabeling and fraudulent resale of synthetic diamonds as natural ones is still a significant risk that has the potential to distort prices and undermine consumer trust.
Global Economic Impacts Of The Shift
As diamond mining scales back, entire economies that depend on it, like Botswana, Namibia, and Russia’s Yakutia region, now face serious economic challenges. Meanwhile, manufacturing hubs in Asia are raking in the benefits of their newfound synthetic diamond exports.
 Christoph Strassler, Wikimedia Commons
Christoph Strassler, Wikimedia Commons
Job Losses In Traditional Mining Regions
The closure or downsizing of diamond mines could leave thousands of miners unemployed. While this has always been a feature of the mining industry, the social impact hits especially hard in regions where mining is one of the few stable sources of income for local communities.
The Future Of Diamond Mining
Experts believe diamond mining will go on but at a smaller scale, focusing on niche markets and luxury collectors. Future operations may place a premium on heritage branding, ethical sourcing, and traceability rather than sheer volume of stones and carats.
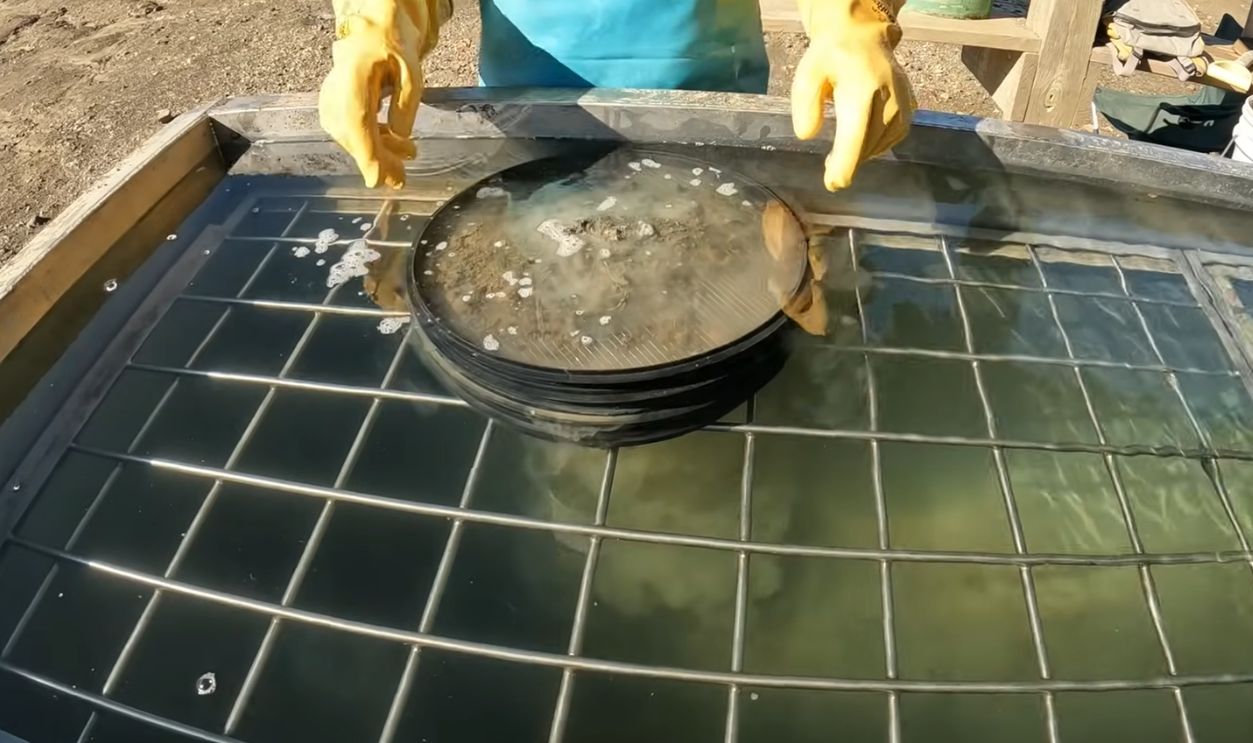 FULL of DIAMONDS! This is HOW - Mining Diamonds, ColoradoGoldCamp
FULL of DIAMONDS! This is HOW - Mining Diamonds, ColoradoGoldCamp
Consumer Education And Transparency
Transparency is becoming a cornerstone of both mined and lab-grown diamond marketing. Clear labeling, sustainability reports, and blockchain traceability tools are now in use as ways to reassure consumers about authenticity and ethics.
Price Volatility And Market Correction
As more lab-grown diamonds flood onto the market, prices have dropped sharply. The oversupply has led to market corrections and dwindling profit margins, generating uncertainty over the long-term sustainability of smaller producers.
 HOW DIAMONDS GROW | UNBOXING LAB GROWN DIAMONDS, Gemstones
HOW DIAMONDS GROW | UNBOXING LAB GROWN DIAMONDS, Gemstones
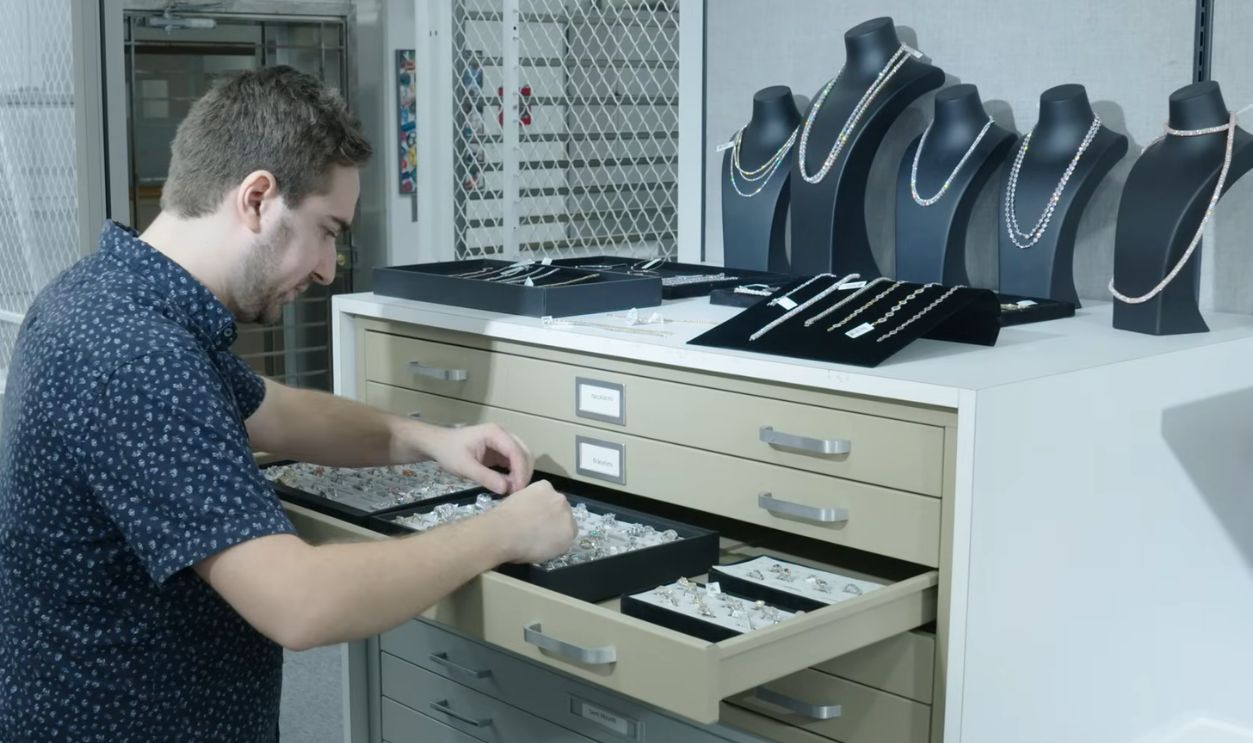
Synthetic Producers: Problems On The Horizon
With falling prices, synthetic diamond manufacturers risk setting off a ‘race to the bottom.’ Some producers may cut corners on quality or environmental standards, making the industry as a whole vulnerable to scandals that could damage their credibility.
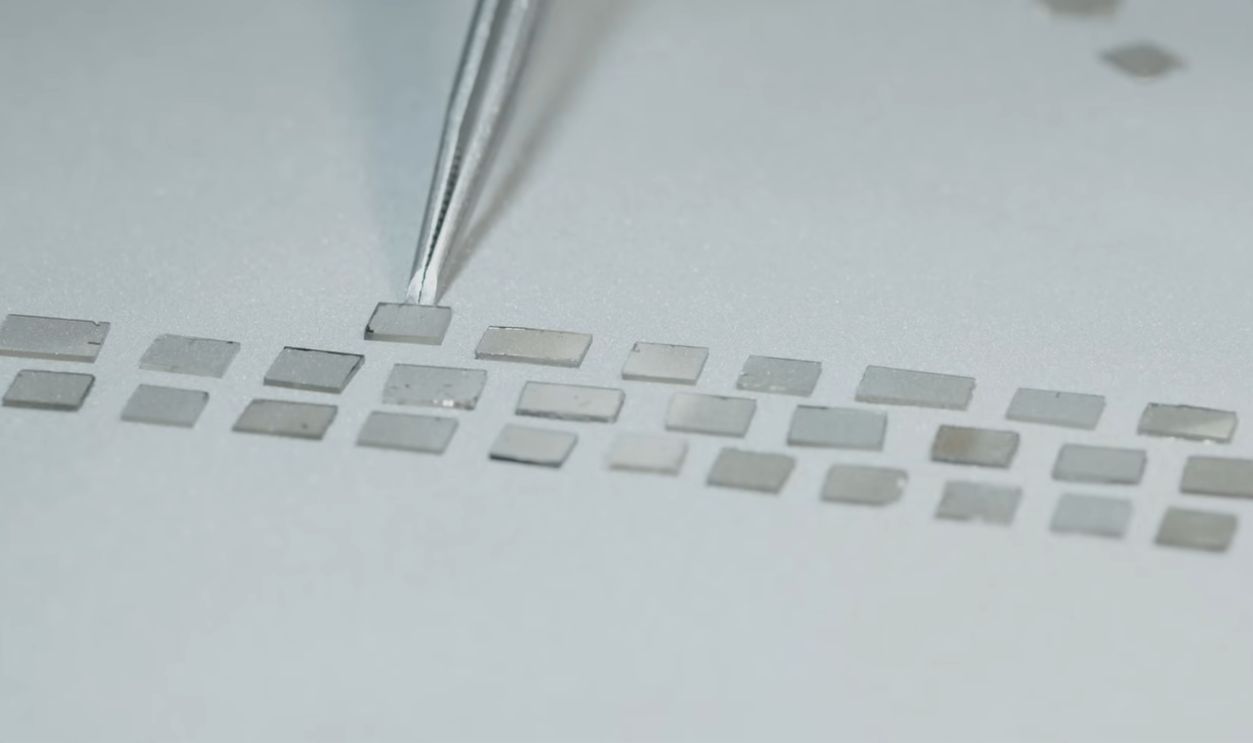 HOW DIAMONDS GROW | UNBOXING LAB GROWN DIAMONDS, Gemstones
HOW DIAMONDS GROW | UNBOXING LAB GROWN DIAMONDS, Gemstones
Innovation And The Next Step
Future innovations may include colored lab-grown diamonds, carbon-negative production processes, and new branding strategies. The industry’s success will depend on balancing ethical production with profitability and consumer trust.
 HOW DIAMONDS GROW | UNBOXING LAB GROWN DIAMONDS, Gemstones
HOW DIAMONDS GROW | UNBOXING LAB GROWN DIAMONDS, Gemstones
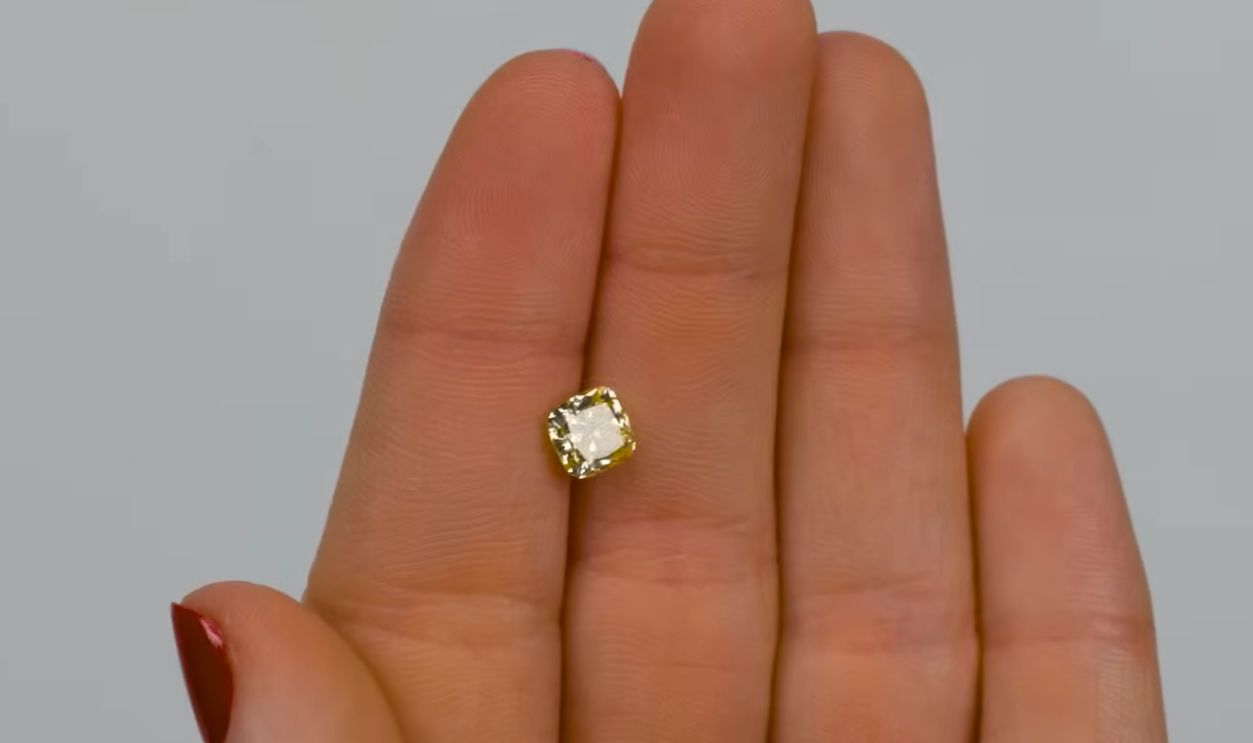
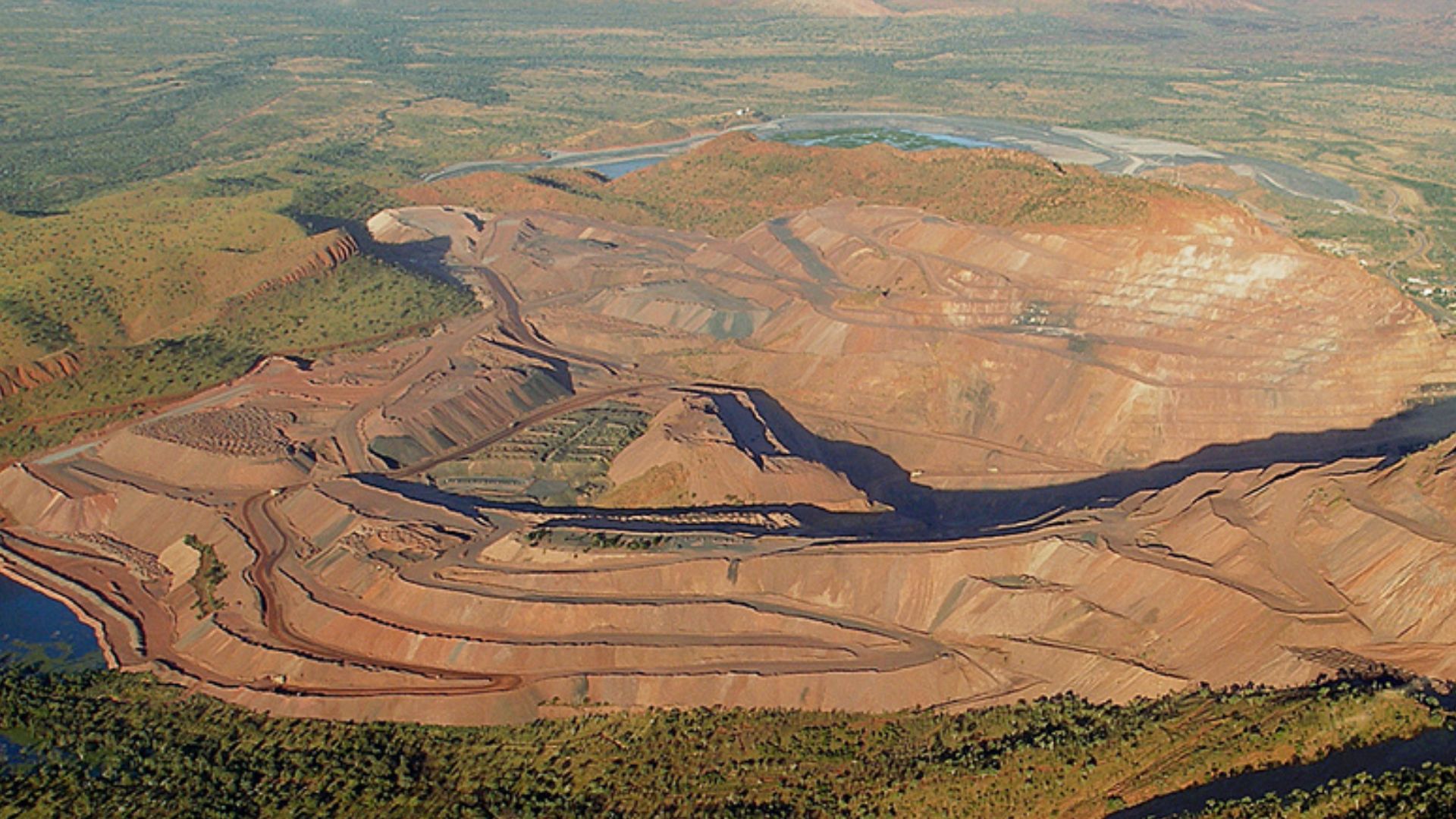
Will Mining Eventually Disappear?
Some analysts believe diamond mining could end altogether within 50 years as existing mines are exhausted and synthetic demand dominates. But as we mentioned above, luxury buyers, heritage collectors, and high-end jewelers will probably preserve room for a niche market in natural stones.
 Brian W. Schaller, Wikimedia Commons
Brian W. Schaller, Wikimedia Commons
An Evolving Symbol Of Value
The diamond was once the ultimate symbol of rarity, but technology is now transforming its role in our culture and economy. Whether the stones are mined or manufactured, their value is now found as much in transparency, ethics, and innovation as in beauty or carat weight.
You May Also Like:
How To Purchase The Perfect Wedding Ring














