The Boom Meets Resistance
Across the U.S., artificial intelligence data centers are multiplying at record speed, driven by cloud giants like Microsoft, Amazon, and Google. But a lot of towns and local governments have started to push back. A growing number of communities are refusing to approve new AI facilities because of worries about energy strain, noise, and environmental costs.
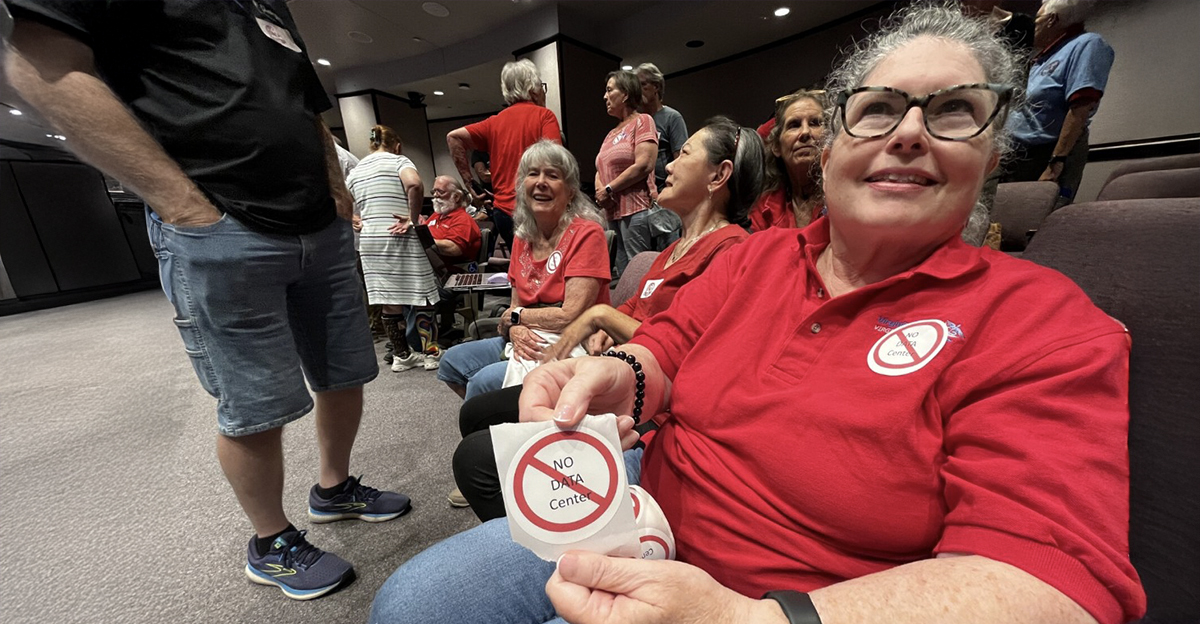

Why AI Needs So Much Power
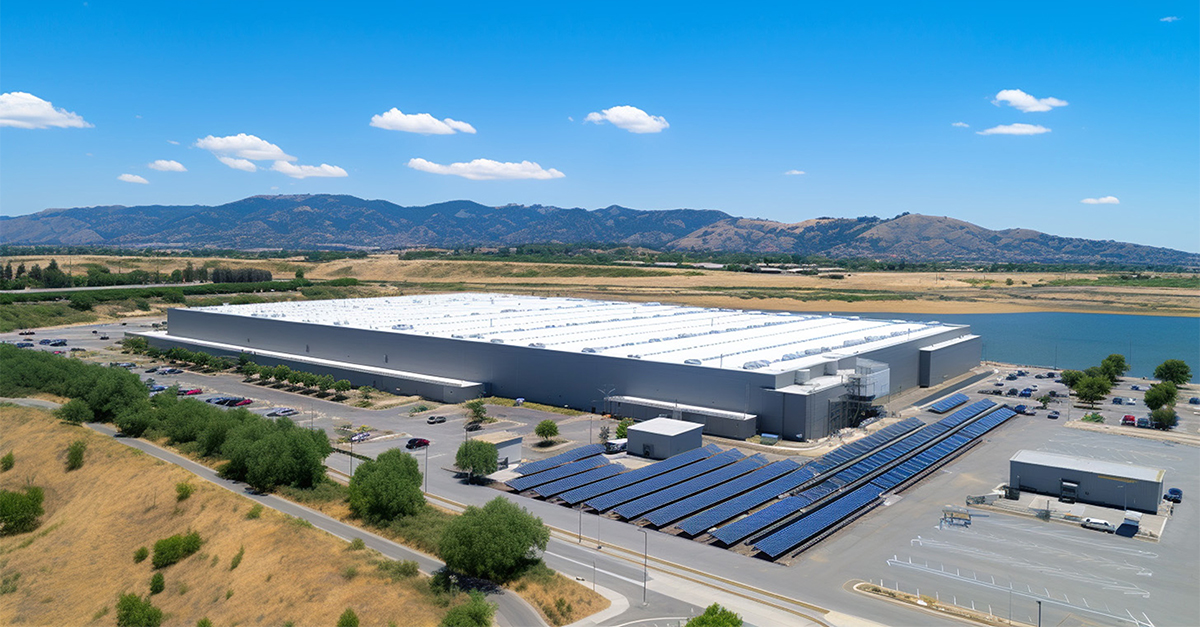
AI data centers aren’t the same as standard server farms because they require exponentially more computing power to train and run large language models (LLMs). According to IBM, each data center can draw as much power as tens of thousands of homes, forcing utilities to rethink grid capacity.
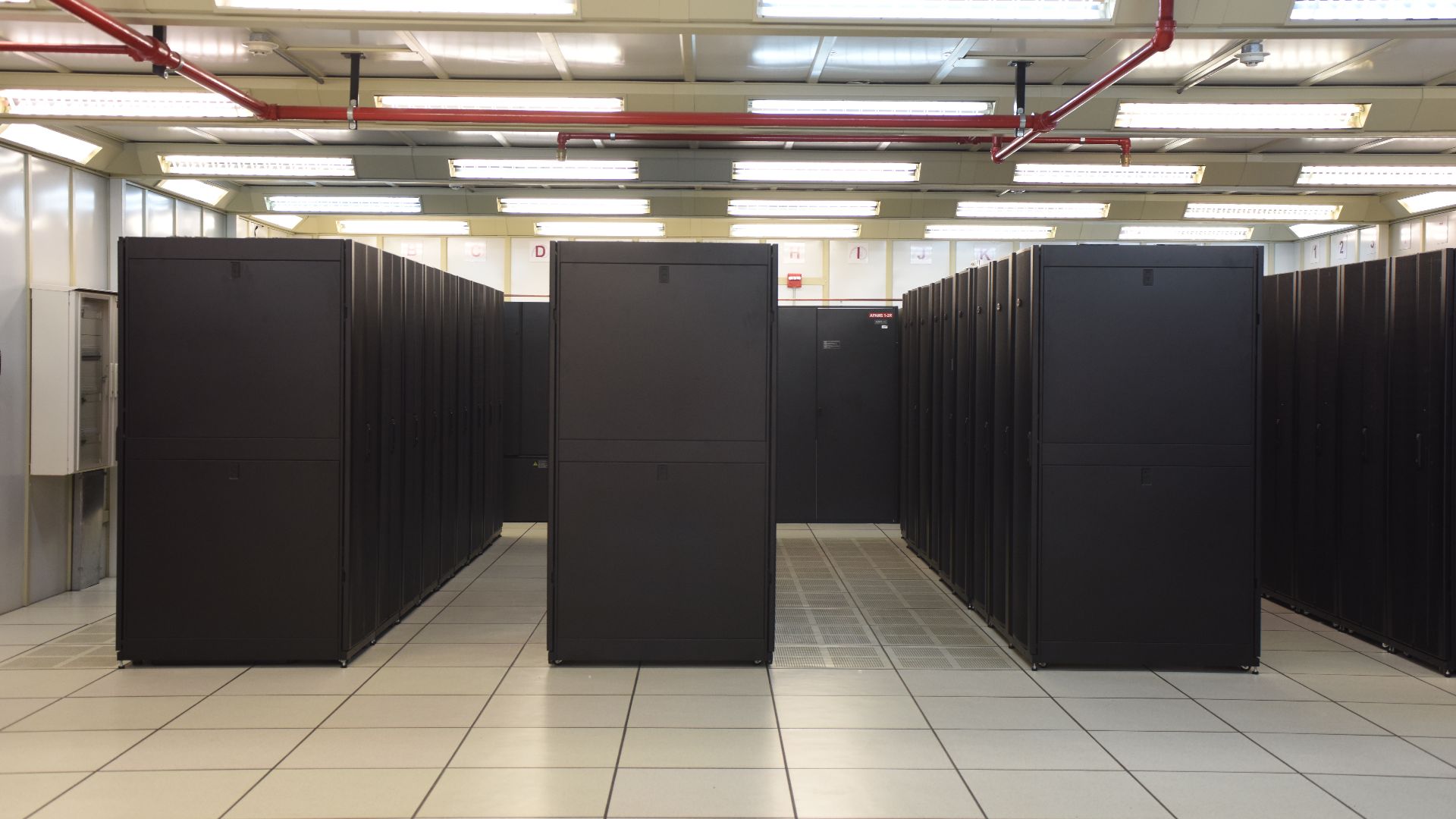 IMarcoHerrera, Wikimedia Commons
IMarcoHerrera, Wikimedia Commons
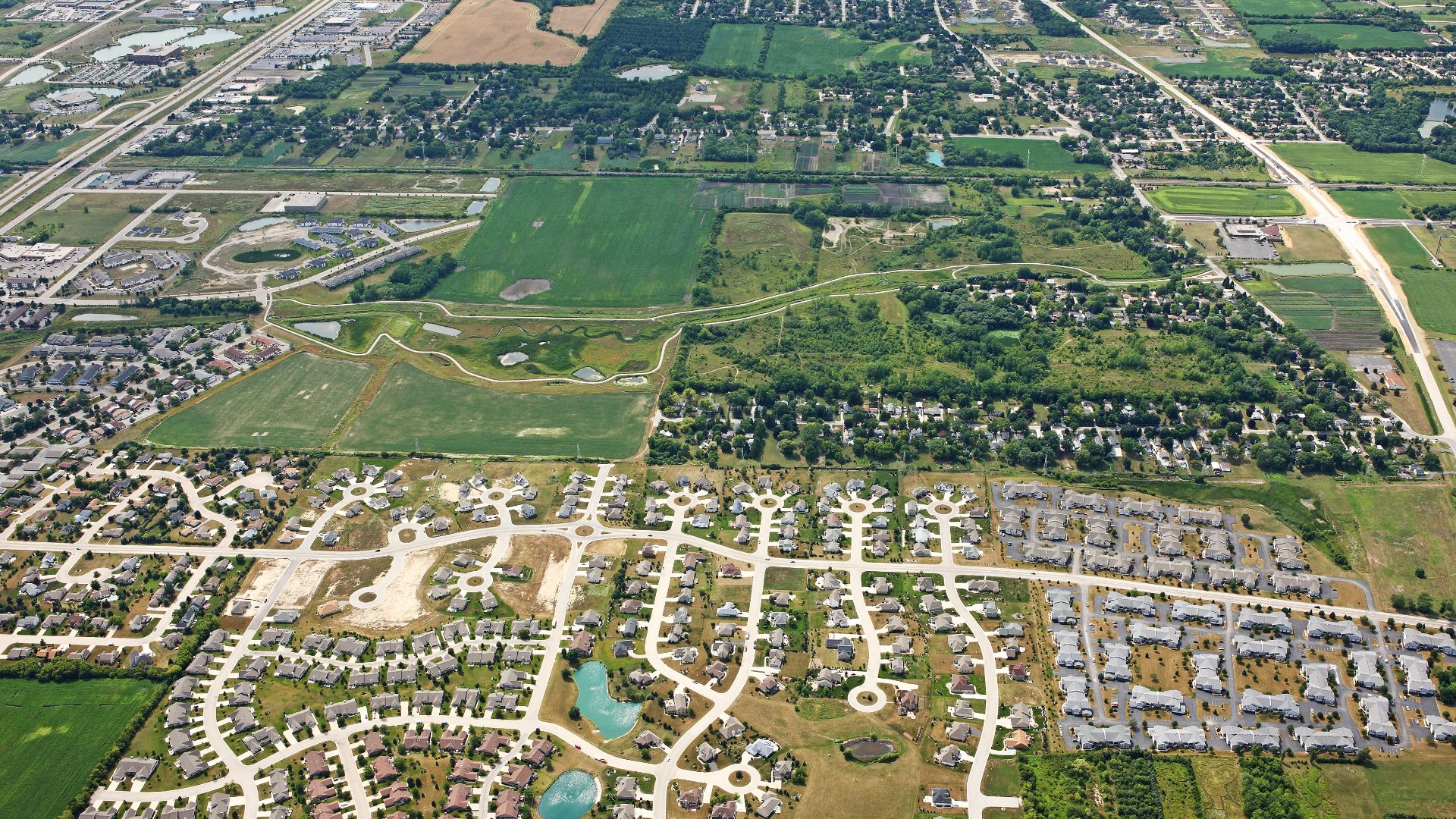
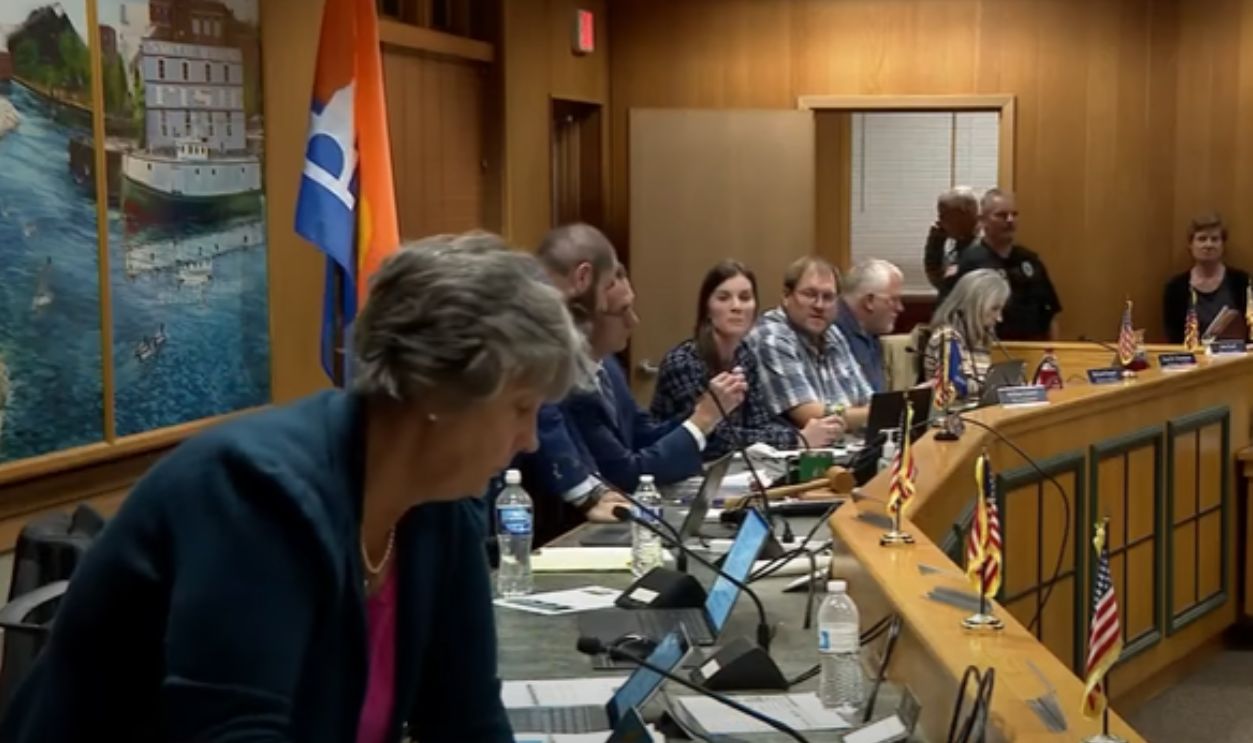
The Michigan Township Lawsuit
In Michigan, the township of Saline is being sued by a developer after blocking an AI data center proposal that residents argued would wreck the rural character of the community. Locals pointed out noise from cooling systems and worries that property values would plummet, prompting a tense legal fight over zoning laws.
 Michael Barera, Wikimedia Commons
Michael Barera, Wikimedia Commons
Wisconsin Pulls the Plug
Microsoft abruptly canceled plans for a data center in Caledonia, Wisconsin earlier this year after community protests and shifting local policies. The cancellation highlighted how volatile public support has become, even for projects promising jobs and infrastructure investment. Microsoft is still going ahead with plans for another data center in the nearby industrial park of Mount Pleasant.
The Virginia Epicenter
Virginia, long known as “Data Center Alley,” has seen residents revolt against constant construction. NPR reported that locals in Prince William and Loudoun Counties say they can’t escape the hum of cooling fans, light pollution, and ever-expanding high-voltage transmission lines.
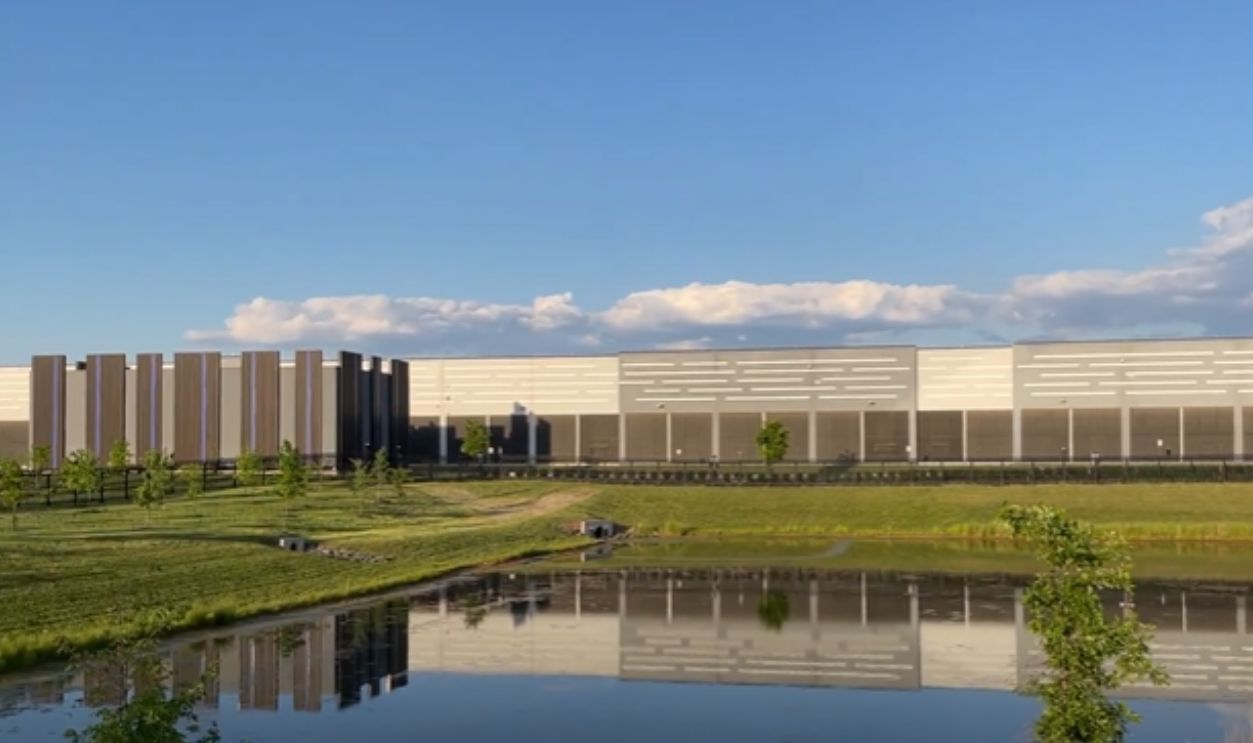 Data Center Alley: Ashburn, Virginia, DgtlInfra
Data Center Alley: Ashburn, Virginia, DgtlInfra
What Drives Local Opposition
For many communities, the issue isn’t only increased noise or traffic, but the project scale. AI data centers can span hundreds of acres, consuming enormous water and power resources while providing relatively few permanent jobs. This makes many communities question whether the trade-off is worth it.
 Inside the World's Largest AI Supercluster xAI Colossus, ServeTheHome
Inside the World's Largest AI Supercluster xAI Colossus, ServeTheHome
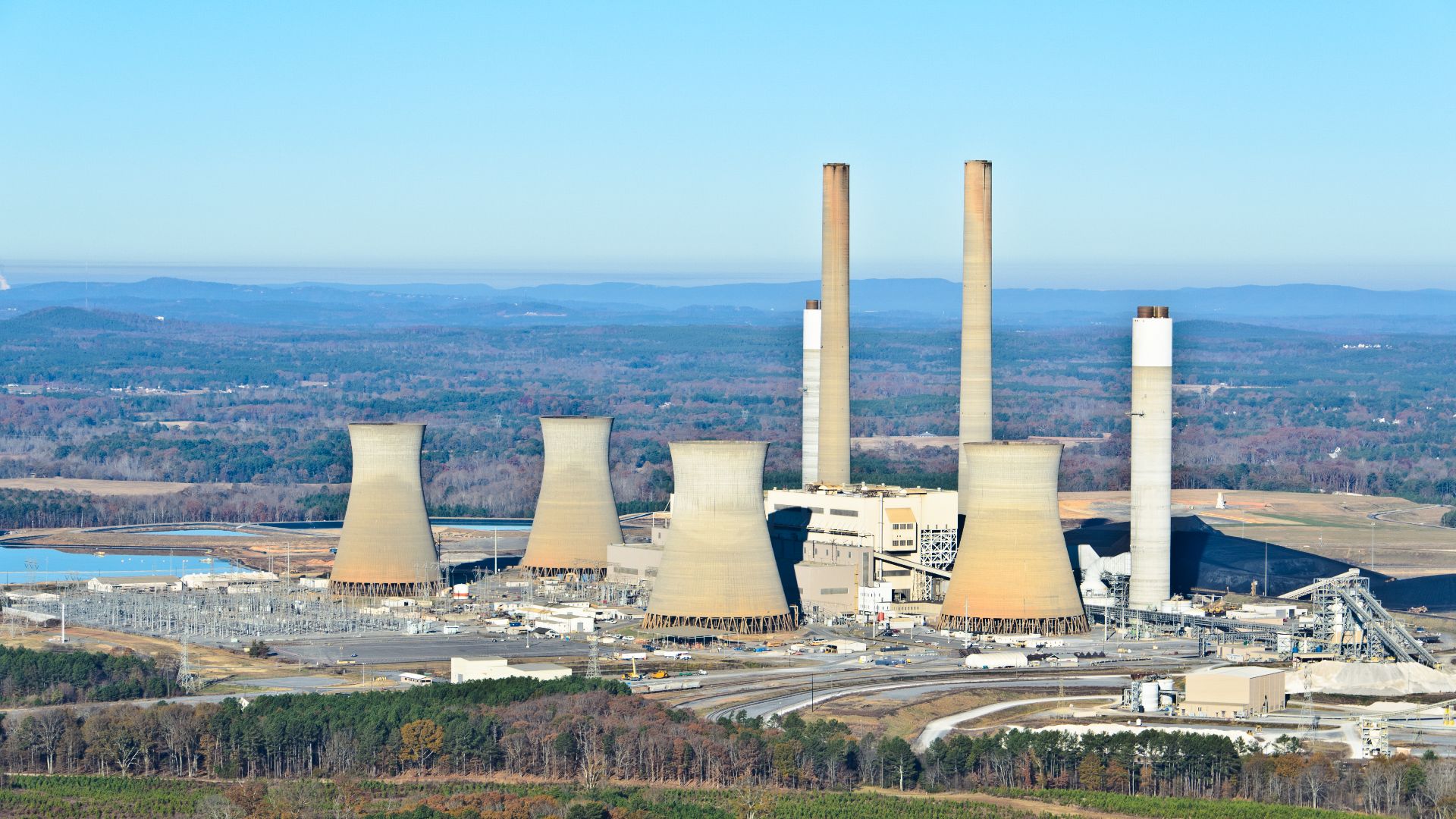
Environmental Worries Grow
Environmental activists argue that data centers amplify carbon emissions right at the same time that states are trying to meet greenhouse gas emissions targets. Each megawatt of power consumed means higher fossil fuel demand unless it’s paired with renewable energy sources, which still have a long way to catch up.
Strain On Local Power Grids
Finance Yahoo reports that the US grid is already under record pressure, and AI’s growth is “completely upending” recent long-term energy forecasts. Utilities warn of regional shortages and skyrocketing infrastructure costs that could drive the price of electricity even higher.
The Rising Cost of Electricity
The same report showed that nationwide power demand from AI and cloud computing could lead to a 20% increase in power consumption within five years. Residential customers are starting to feel the impact as utilities file for rate hikes to cover the costs of grid expansion.
Water: The Hidden Resource
A lot of communities are also concerned by the heavy use of water by data centers. Cooling systems in AI centers can consume millions of gallons per day, especially in arid regions, leading to local moratoriums in states like Arizona and Texas where drought conditions are a common occurrence.
 Water usage by AI data centers sparks concerns | NewsNation Now, NewsNation
Water usage by AI data centers sparks concerns | NewsNation Now, NewsNation
Cities Drawing the Line
According to CNET, cities like Santa Clara, California, and Hillsboro, Oregon, are starting to cap new data center development. Local governments say their electrical substations and cooling capacity are maxed out, forcing planners to shift their priorities back to housing and small business growth.
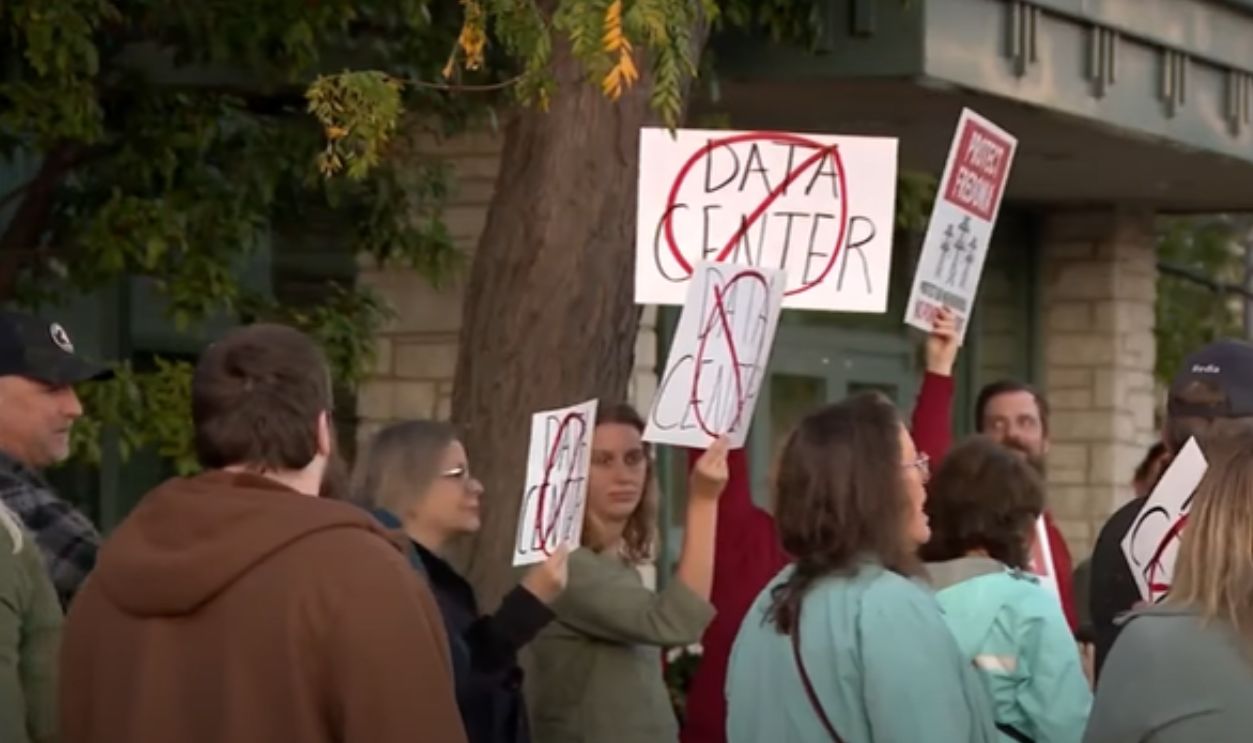 Data center project protests, WISN 12 News
Data center project protests, WISN 12 News
Fear of Becoming A Server Town
People in fast-growing suburbs worry that their communities might turn into “server towns” — industrial zones filled with hulking windowless buildings. The visual and environmental footprint is making city planners rethink whether these kinds of projects fit in with their long-term urban goals.
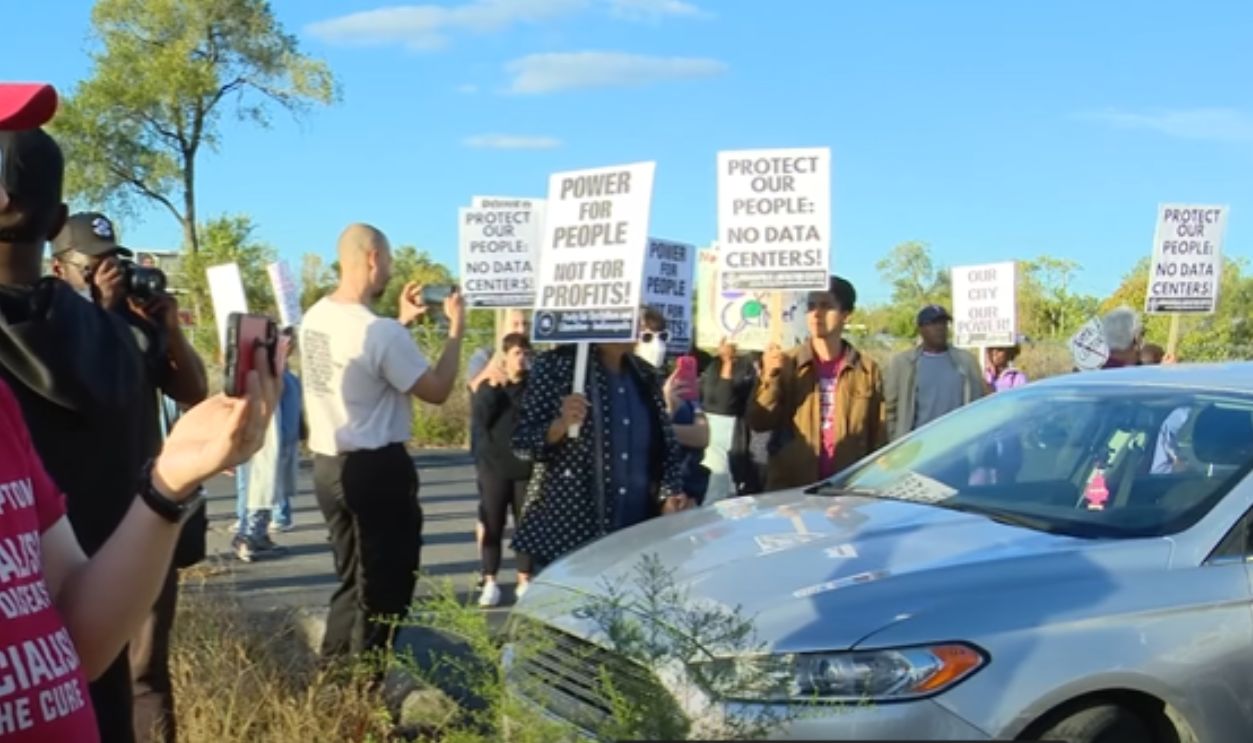 Frustrated neighbors protest proposed 13-acre data center in Martindale-Brightwood, WTHR
Frustrated neighbors protest proposed 13-acre data center in Martindale-Brightwood, WTHR
Energy Inequality Grows
As utilities divert massive amounts of energy to AI facilities, ordinary consumers face reliability concerns. Smaller towns argue that mega-corporations shouldn’t get preferential access to electricity while local development suffers rolling blackouts or grid limitations.
The Legal Showdowns Begin
The Washington Post recently reported on new lawsuits where developers are challenging bans and moratoriums as unconstitutional. The fights are testing whether localities can legally restrict facilities critical to the country’s technology infrastructure.
What Tech Giants Are Saying
Microsoft, Amazon, and Google argue that these facilities are essential to America’s economic competitiveness. They claim they’re investing in renewable energy and more efficient cooling systems. But critics insist those efforts don’t offset the immediate strain on local grids.
Green Promises Vs Reality
While a lot of companies make up-front pledges of carbon neutrality, the build-out is outstripping renewable supply. Even “clean” AI data centers rely on grids still powered in large part by natural gas and coal, raising doubts about their claims of sustainability.
 erwinboogert, Wikimedia Commons
erwinboogert, Wikimedia Commons
State Incentives Under Scrutiny
Many states have offered up tax breaks and infrastructure subsidies to attract data center projects. Now, under pressure from their own residents and environmental groups, some legislators are having second thoughts about those incentives, arguing that they benefit corporations more than citizens.
 Data center project protests, WISN 12 News
Data center project protests, WISN 12 News
The Ripple Effect on Housing and Roads
In regions like Northern Virginia, the steady expansion of data centers has clogged roads and consumed valuable real estate once zoned for residential use. Homeowners say the industrial sprawl has changed the character of their neighborhoods into something they no longer recognize.
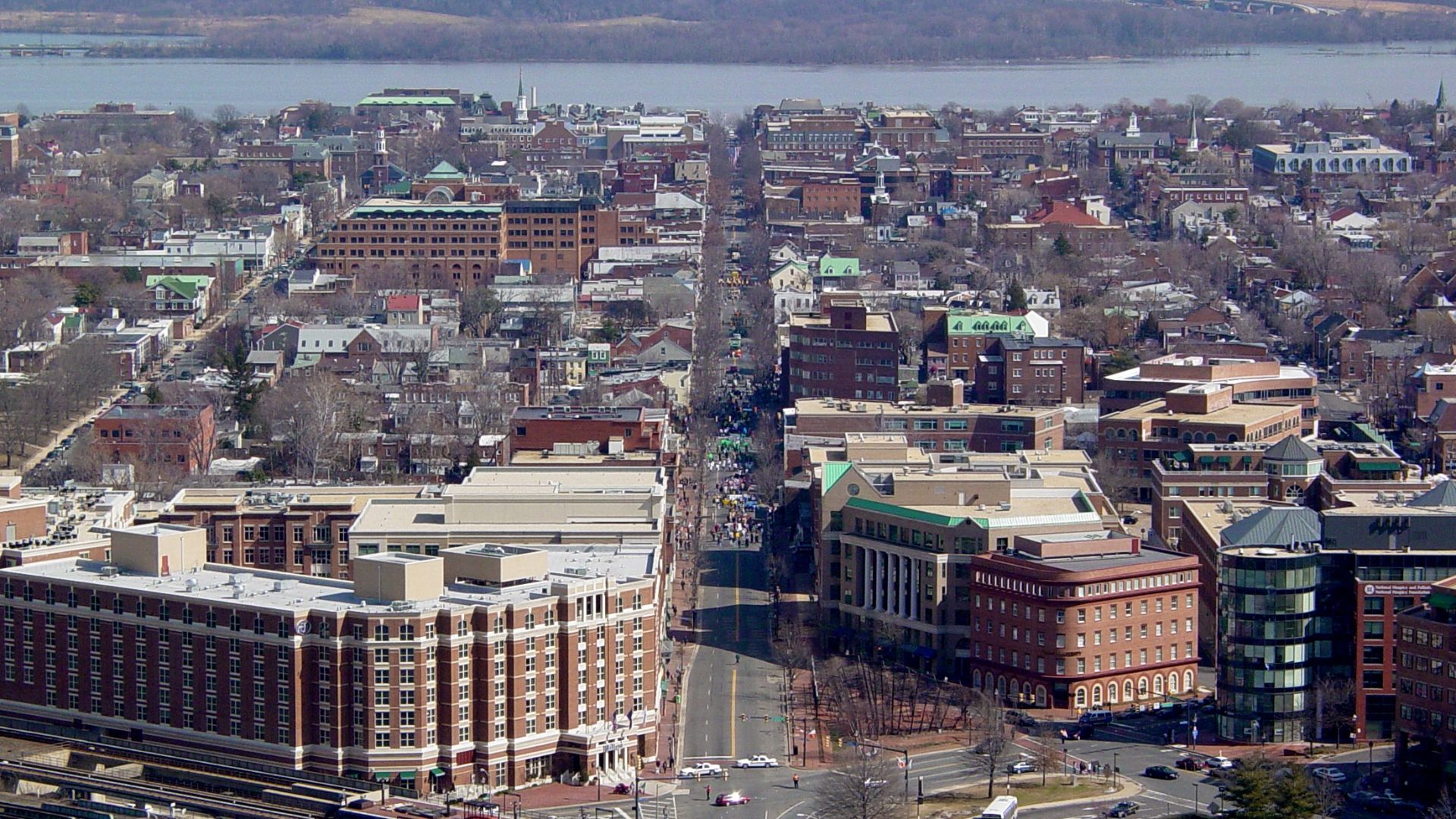 Ben Schumin, Wikimedia Commons
Ben Schumin, Wikimedia Commons
The Political Dimension
Data center opposition often cuts across party lines. Conservatives warn of foreign corporate control of critical power infrastructure, while liberals tend to focus on environmental problems, sustainability, and corporate overreach.
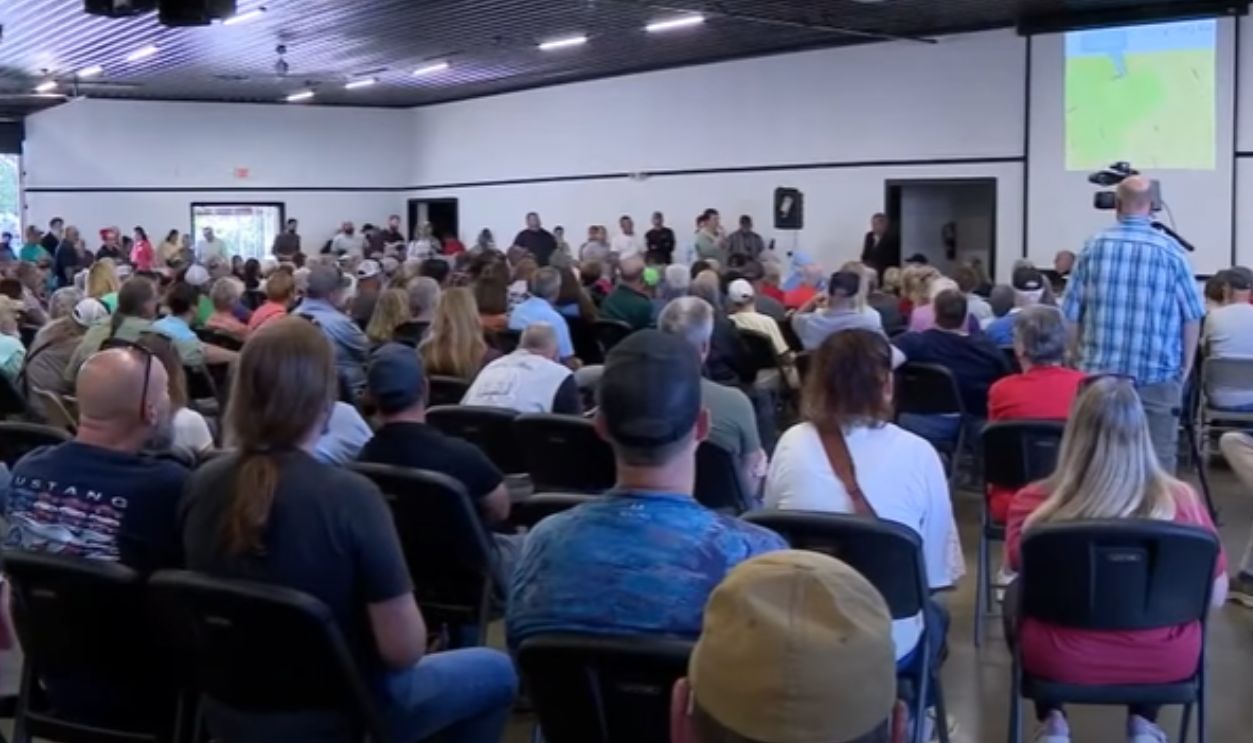 Meade County residents oppose data center proposal, WLKY News Louisville
Meade County residents oppose data center proposal, WLKY News Louisville
The Push For Federal Guidelines
Experts say federal standards may soon be needed to manage the development of data centers. For the time being, zoning, noise limits, and energy policies are all managed locally, creating a patchwork of approvals, delays, and lawsuits that could slow the AI revolution to a crawl.
 Managing Data Center Environmental Sustainability, EPI Data Centre Services
Managing Data Center Environmental Sustainability, EPI Data Centre Services
AI’s Insatiable Appetite For Power
IBM notes that future AI models could require hundreds of billions of parameters, driving computing needs far beyond even today’s limits. Without the development of new infrastructure or breakthroughs in the efficiency of microchips, energy use will continue to rise ever higher.
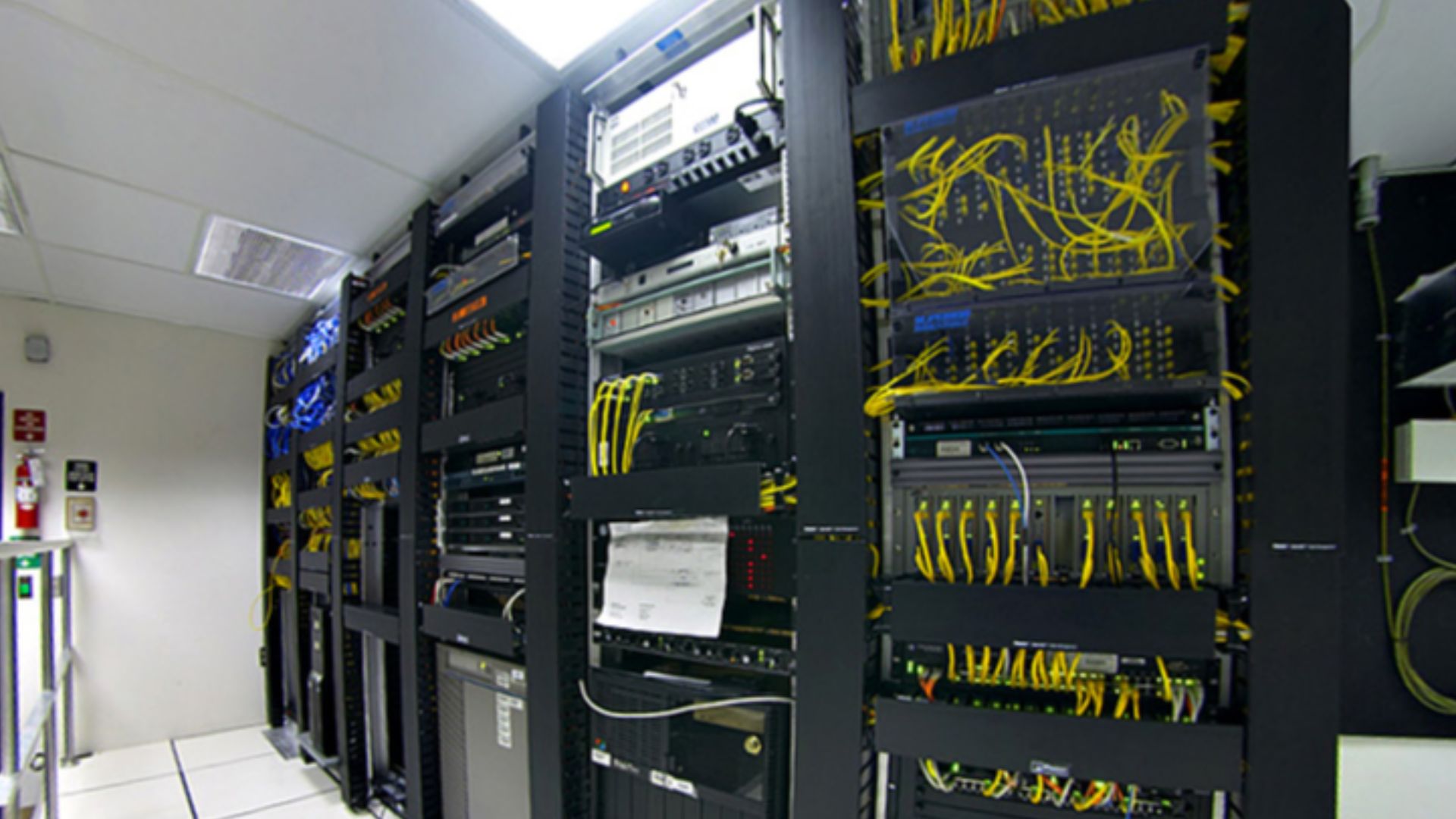 MickStephenson, Wikimedia Commons
MickStephenson, Wikimedia Commons
A Possible Strategy: Rural Relocation
To avoid urban resistance, some companies are scouting out more remote or rural areas with cheaper land and fewer zoning obstacles. But even in these more sparsely settled places, resistance is growing as residents worry about environmental costs with minimal benefit to the community.
 Patrick - Patrick, Wikimedia Commons
Patrick - Patrick, Wikimedia Commons
International Comparisons
Canada and parts of Europe are seeing a similar backlash against data centers, with moratoriums issued in Ireland and the Netherlands. As one Yahoo Canada report outlined, governments abroad are also weighing the security of their energy supply against the promise of digital innovation.
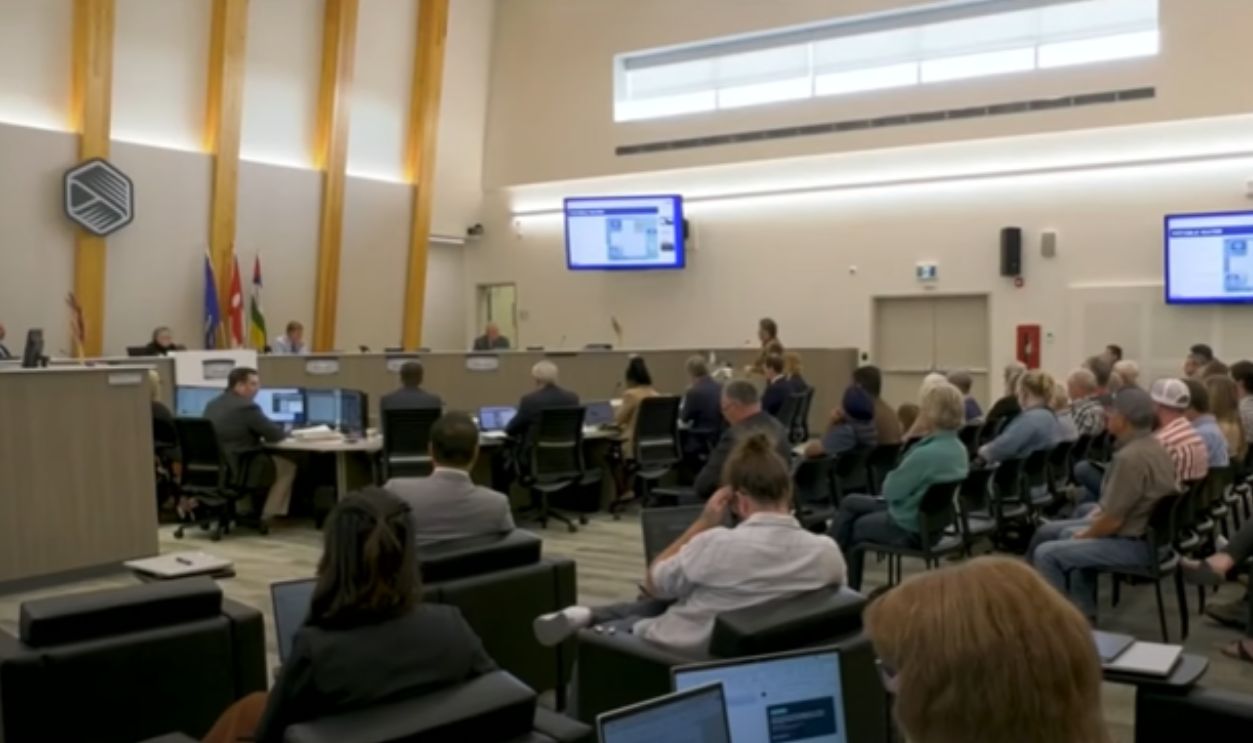 Controversial data centre pitch, CTV News
Controversial data centre pitch, CTV News
The Search For Solutions
Industry leaders are investing in liquid cooling, AI-optimized power management, and renewable co-generation to reduce the incredible demand for power. But the basic problem is still there: AI’s hunger for data and electricity continues to surpass the pace of sustainable expansion.
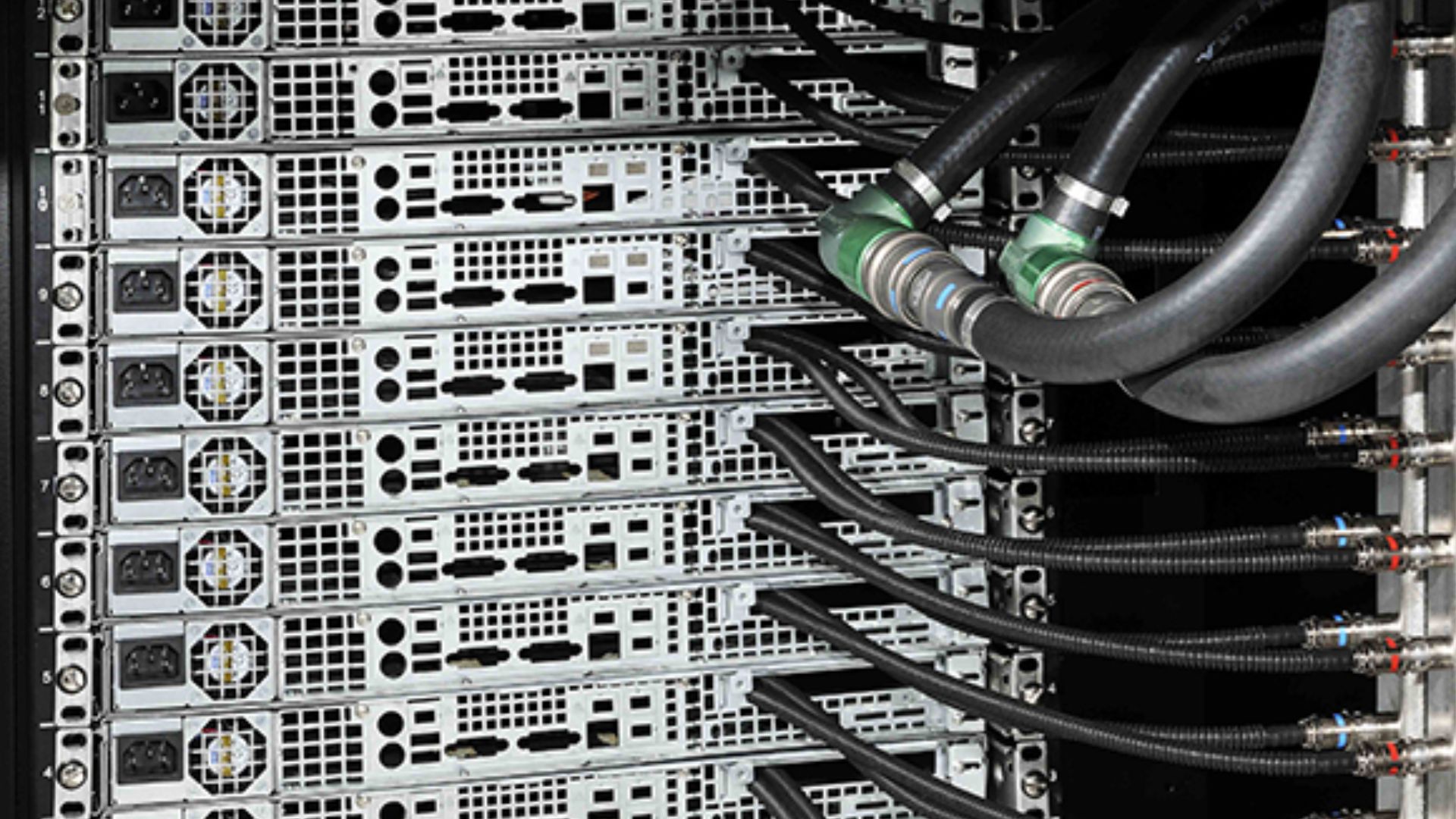 Barbara Massolin, Wikimedia Commons
Barbara Massolin, Wikimedia Commons
A Reckoning Is Coming
Communities that once competed to attract tech investment are now drawing red lines. The question is no longer whether AI data centers can be built. They’re going to go somewhere. The question is where, and at what cost to the public.
 Michael Kauffmann, Wikimedia Commons
Michael Kauffmann, Wikimedia Commons
You May Also Like: